Technical
The Importance Of Oblique Imagery For 3D Modelling
heliguy™ datasets show oblique imagery's value in 3D modelling, we compare it to nadir imagery, and share our top DJI solutions.
Find out about the value of using oblique imagery to build robust and accurate 3D models with drone data;
Oblique imagery is better than nadir imagery for modelling as it captures more detailed information on the sides of structures and objects;
Learn about the best drone solutions for oblique mapping, including the DJI Zenmuse P1 and the Share UAV 203S Pro payloads;
heliguy™ has an in-house surveying department to help clients with 3D modelling advice, hardware and software supply, workflow support, and data processing assistance.
When it comes to creating accurate and realistic 3D models with drone data, oblique imagery is an essential requirement.
Unlike traditional top-down views - known as nadir - oblique imagery captures multiple angles and perspectives, allowing for a more comprehensive and detailed representation of buildings, landscapes, and objects.
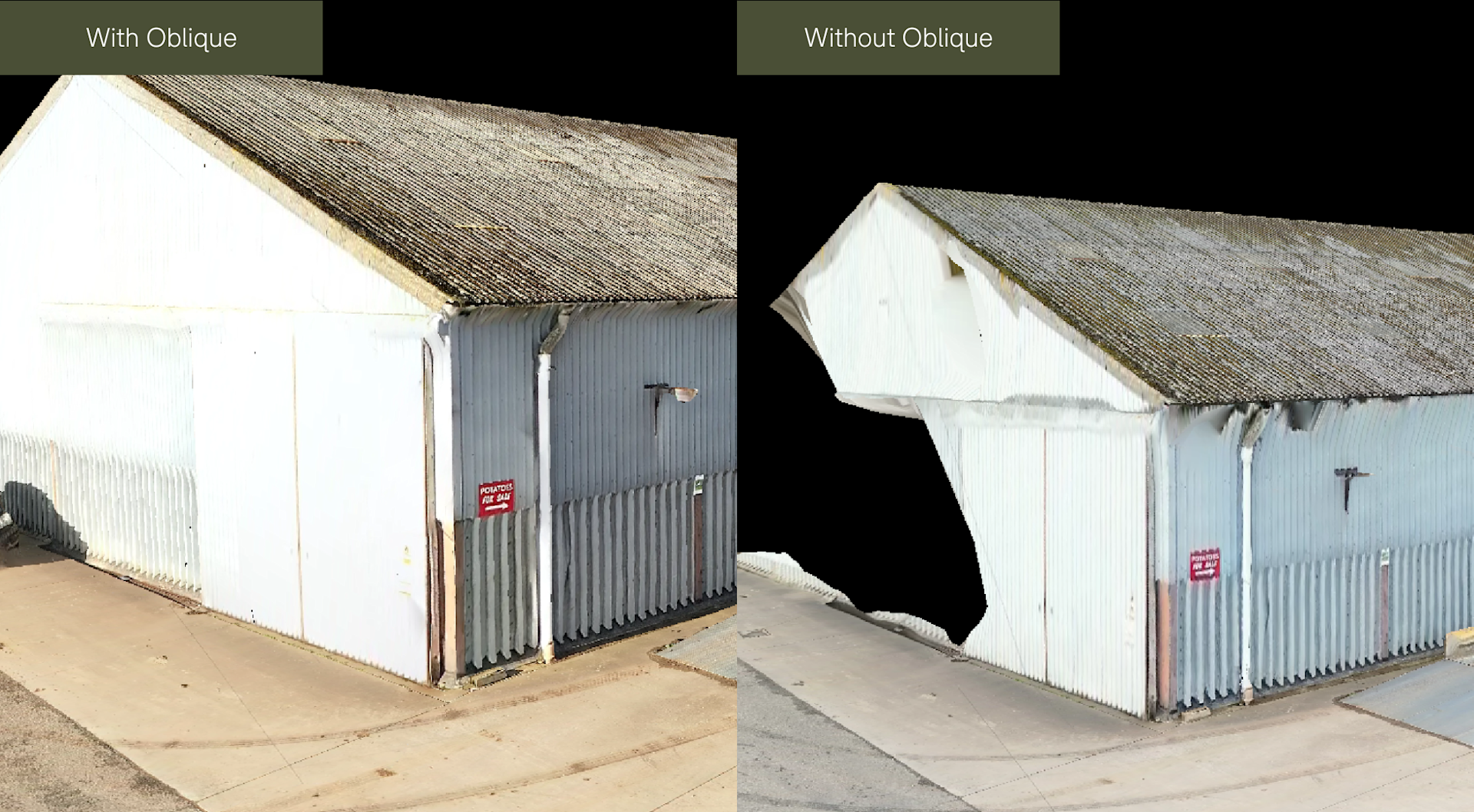
This comparison image - captured with the DJI Zenmuse P1 photogrammetry camera - demonstrates the advantages of using oblique imagery for 3D modelling, compared to just nadir imagery.

This blog takes a deeper dive into the value of oblique imagery for 3D modelling, demonstrates this with further datasets, and highlights the best solutions for streamlined oblique mapping.
heliguy™ has an in-house surveying department to help you adopt and scale drone surveying hardware and assist with data capture workflows and processing.
What Is Oblique Imagery?
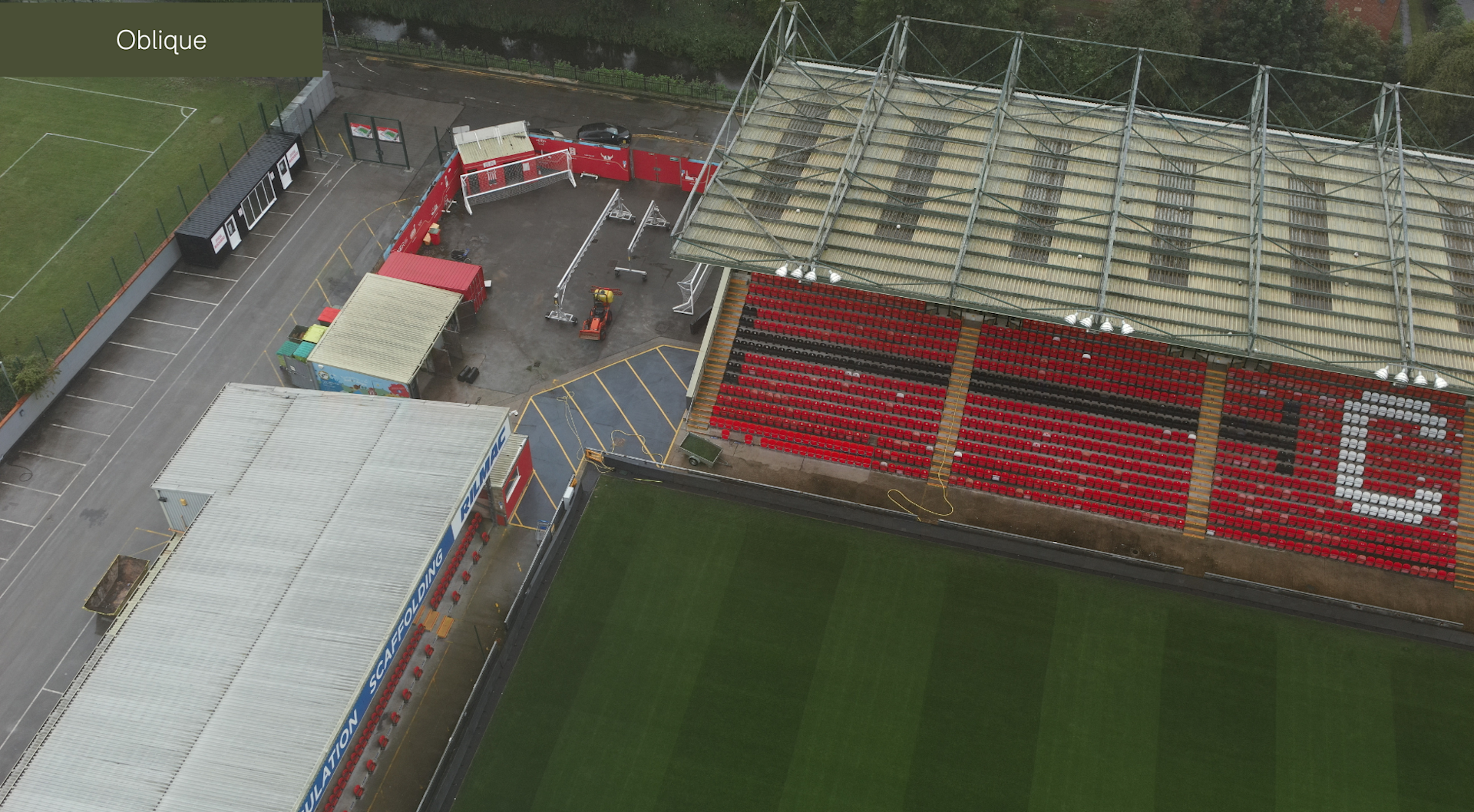
Oblique imagery refers to images taken at an angle, usually between 30 and 60 degrees from the ground - as shown in the image below. This angled view allows more detailed information on the sides of objects.

This differs from nadir imagery, which refers to images captured with the camera pointing directly downward at a 90-degree angle relative to the ground - as illustrated by the below image.
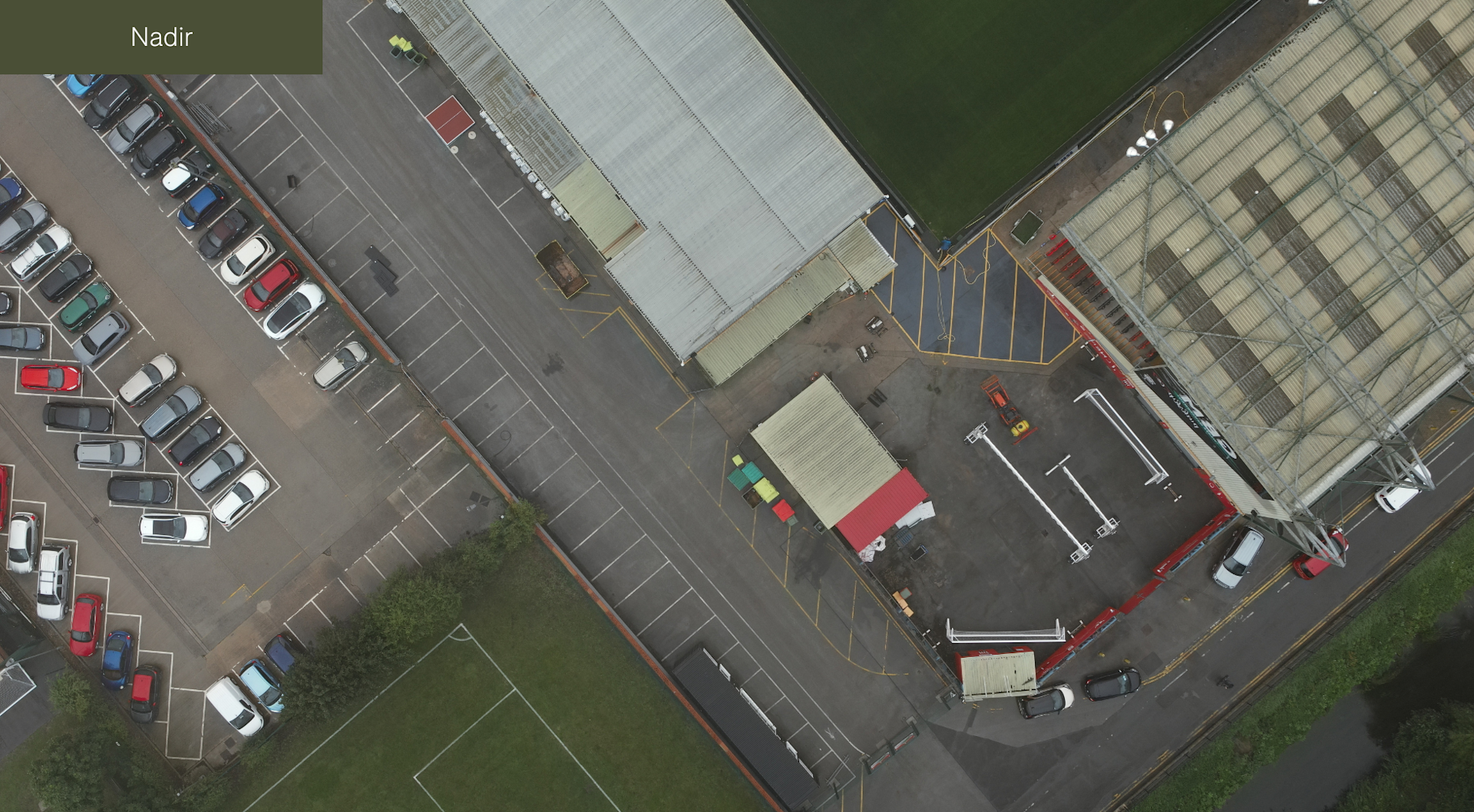

It's worth noting that while nadir imagery is best suited to 3D modelling, it does have its value in drone surveying - specifically for creating detailed orthophotos or othomosaic maps.
Why Oblique Imagery Is Needed For 3D Modelling
3D models are valuable digital assets, providing an immersive, realistic view of structures and landscapes.
This enables precise analysis, improved planning, and better decision-making across industries like construction, urban planning, real estate, and environmental management.

Oblique imagery is crucial to building a robust 3D model. Benefits include:
Captures the Sides of Structures: Oblique imagery captures details that are invisible from a top-down nadir view. The angled views in oblique imagery provide these missing details, which are crucial for rendering realistic models.
Improves Depth Perception and Realism: Oblique images help software 'see' the depth and shape of objects, allowing for more realistic models. This multi-perspective data is necessary for a realistic 3D rendering, giving the model true-to-life proportions and depth - therefore increasing accuracy.
Enables High-Quality Texturing: Texture helps models look realistic and visually appealing. Oblique images capture the texture on walls, rooftops, and other surfaces, allowing for high-quality rendering of materials like stone, brick, glass, or vegetation.
Minimises Blind Spots and Shadows: Using only nadir images can create blind spots, ie areas of the model that lack information because they weren’t visible from a top-down view. By capturing images at multiple angles, oblique photography minimises blind spots and improves visibility on vertical surfaces, resulting in a more complete model.
Provides Contextual Views: Oblique images are excellent for providing spatial context, allowing stakeholders to see not just individual structures but also the surrounding environment. When combined with 3D modeling, these views offer an immersive experience, which is valuable for planning and decision-making.
The table below provides an at-a-glance overview of the key advantages of using oblique data capture for building robust and detailed 3D models.
Nadir Imagery | Oblique Imagery | |
|---|---|---|
Camera Angle | Directly downward (90 degrees) | Angled (typically 45-60 degrees) |
Field of View | Captures ground or roof from top-down perspective | Captures multiple perspectives, including sides |
Detail on Vertical Surfaces | Limited; lacks side details on buildings, cliffs | High; captures walls, facades, and slopes |
Ideal for Ground Mapping | Yes, provides clear, top-down view of area | Not ideal, as perspective angle can distort ground view |
Texture Quality On Surfaces | Limited texture detail due to single perspective | Excellent texture detail with realistic depth |
Suitability For 3D Modelling | Limited for detailed models; lacks side views | Essential for full, accurate 3D models |
Image Distortion | Minimal distortion; flat view | Increased at edges; provides depth perception |
Photogrammetry Data | Less data for vertical measurements | Rich data for height, depth, and volume calculations |
Realism Of 3D Models | Lacks realism; flat with limited structure | High realism; captures object shapes from all sides |
3D Model Accuracy | Limited accuracy due to single angle | High accuracy with multi-angle perspectives |
However, using both types of imagery can provide a comprehensive dataset: Nadir imagery for clear, precise top-down angles, and oblique imagery to capture the depth, height, and structure essential for realistic 3D modeling.
The image below shows the different cameras angles during a flight collecting both nadir and oblique imagery
Oblique Vs Nadir: Dataset Examples
Data collected by the heliguy™ in-house surveying team with the DJI P1 photogrammetry camera illustrate the differences between a 3D model with oblique imagery, and without.
For instance, look at the increased level of detail on the model containing oblique imagery, compared to the dataset comprising only nadir imagery. In the oblique dataset, the wall and door and more defined and complete.
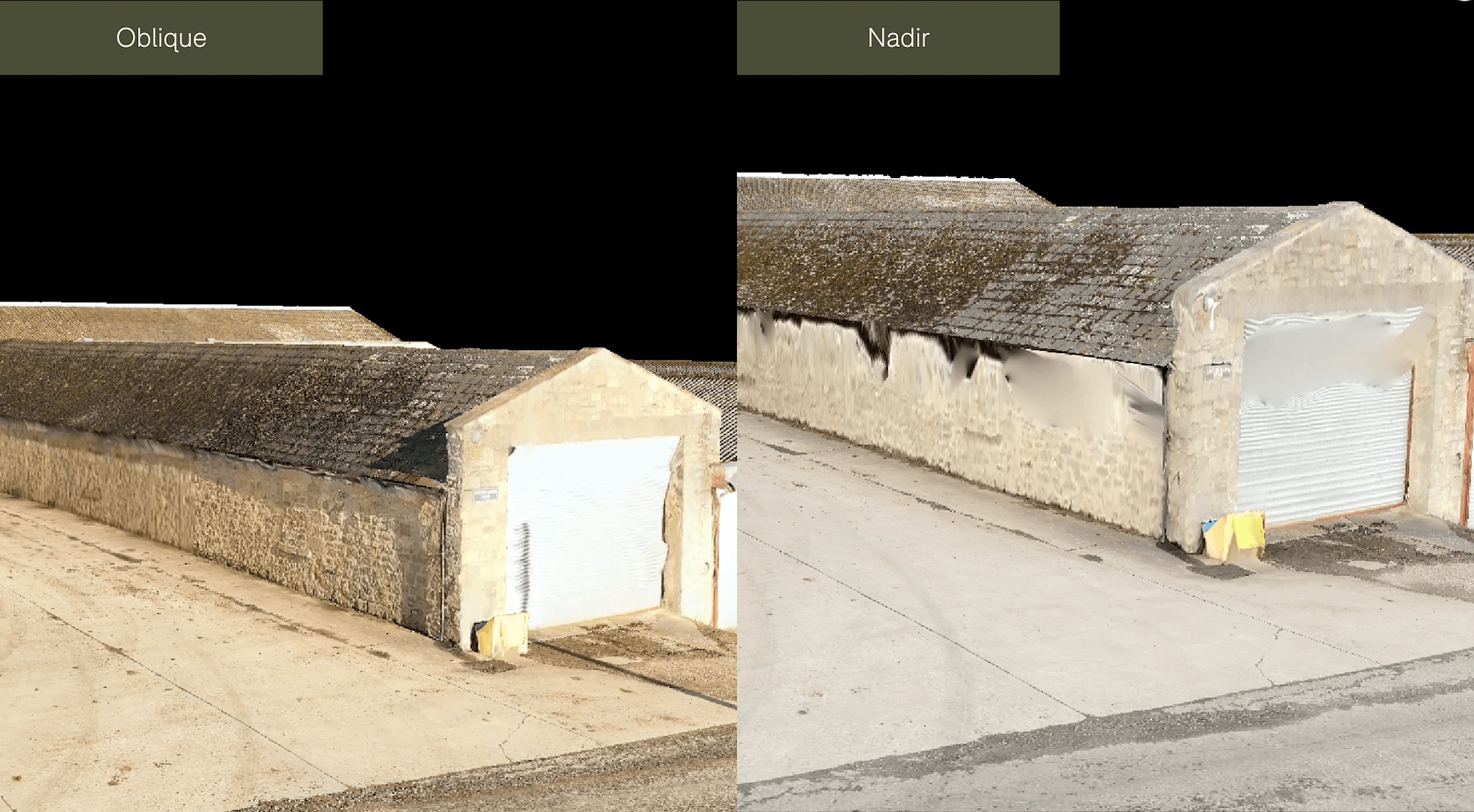

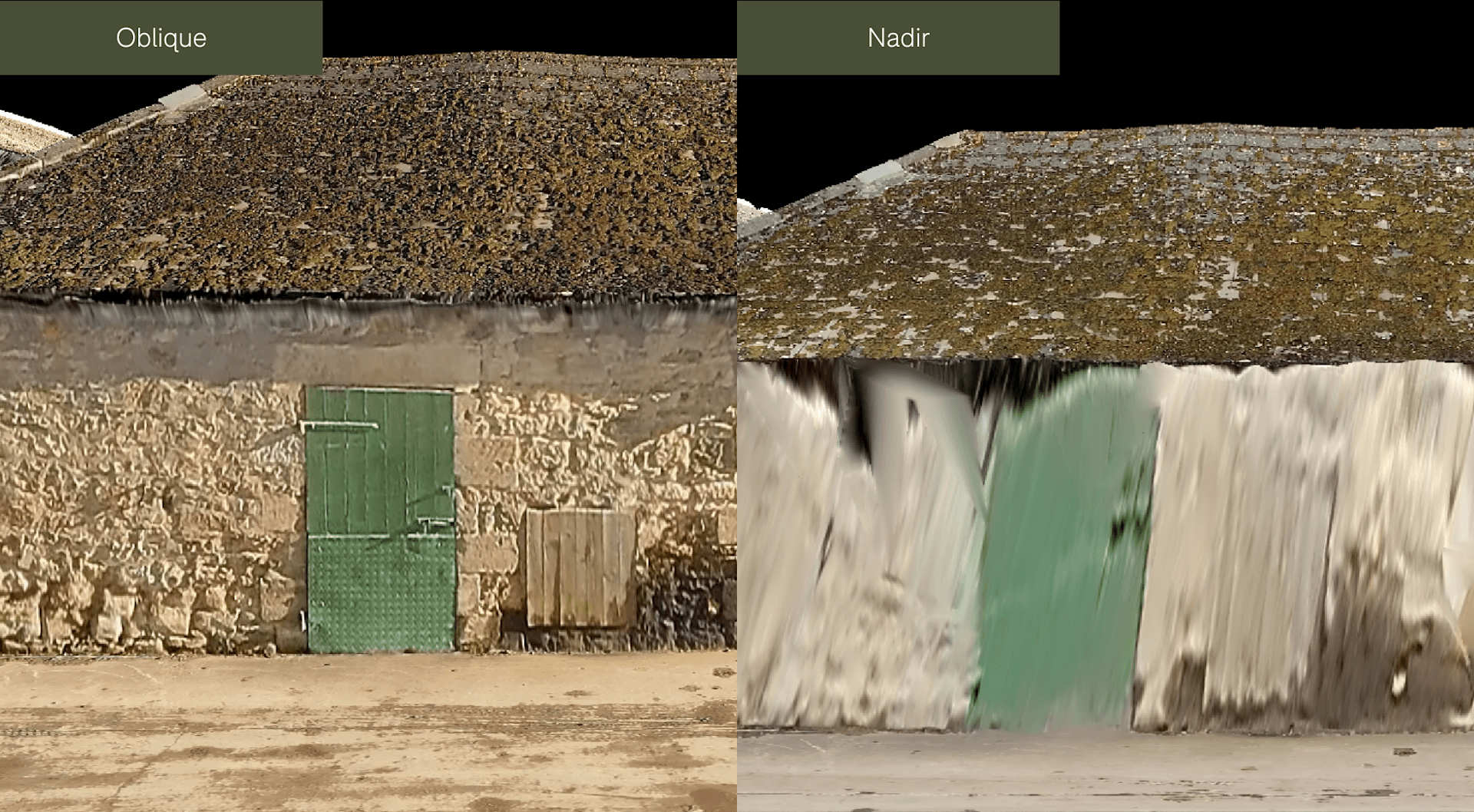
And in these comparison pictures, the level of texturing detail on the bricks is significantly higher than the dataset using only nadir imagery.

Industry-applications For Oblique Drone Imagery
Oblique imagery-based 3D modeling has become a go-to method for professionals in numerous fields. Examples include:
Construction and Architecture: Detailed 3D models aid in project planning, site analysis, and monitoring progress on construction sites.
Urban Planning and Smart Cities: High-resolution models help urban planners visualise city layouts, assess infrastructure, and plan for future developments.
Historical Documentation: For preservation efforts, 3D models created with oblique imagery provide accurate representations of heritage sites and buildings.
Real Estate Marketing: Realistic 3D models give potential buyers an immersive view of properties, showing them what to expect from every angle.
Emergency Response: In post-disaster scenarios, 3D models generated from oblique imagery allow responders to assess damage and navigate affected areas with clarity.
Best Oblique Drone Mapping Cameras
So, what are the best oblique drone mapping cameras available? The list below highlights a collection of industry-leading solutions - all of which can be supplied by heliguy™.
DJI Zenmuse P1
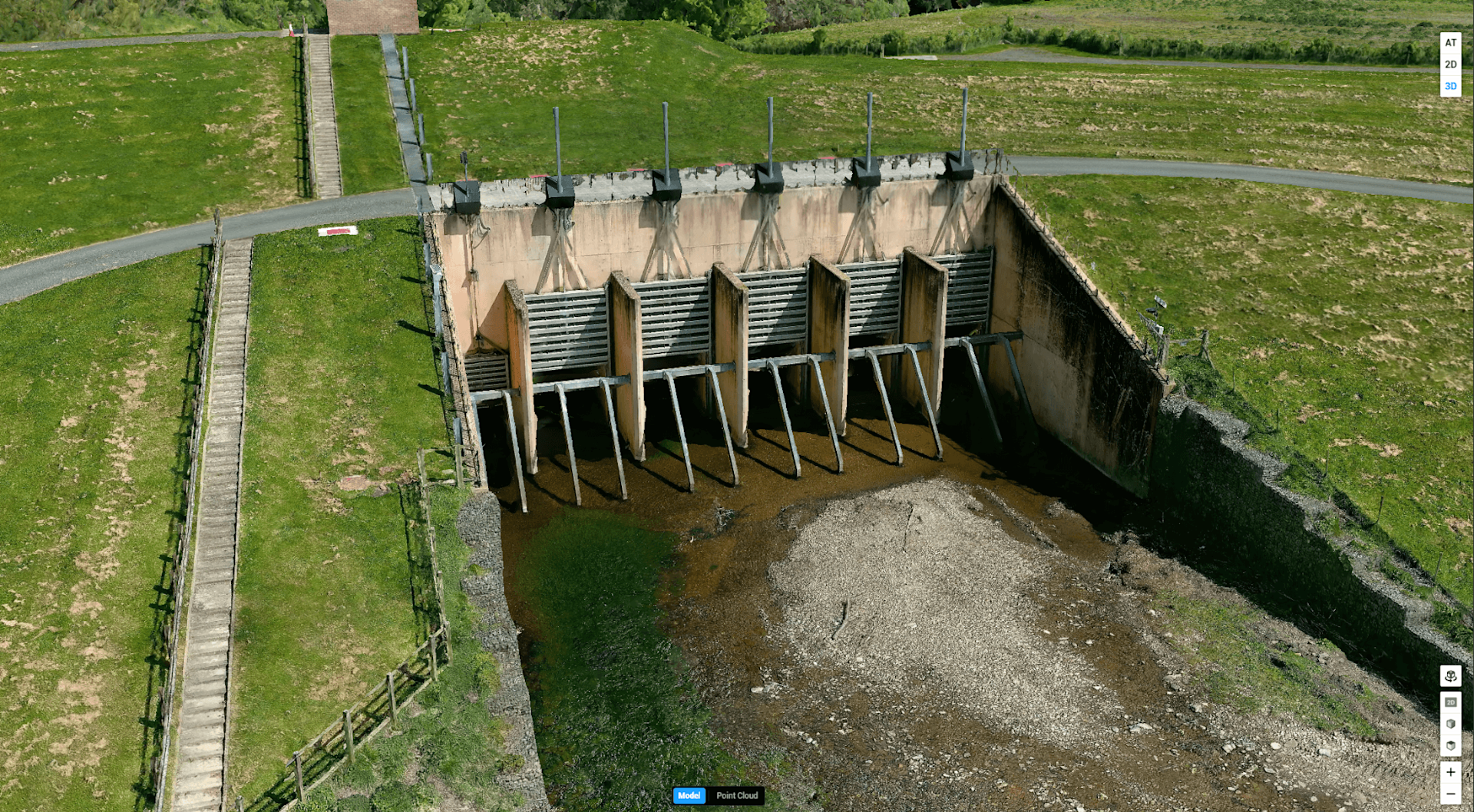
The DJI Zenmuse P1 is a 45MP photogrammetry camera, compatible with the DJI M350 RTK and DJI M300 RTK.
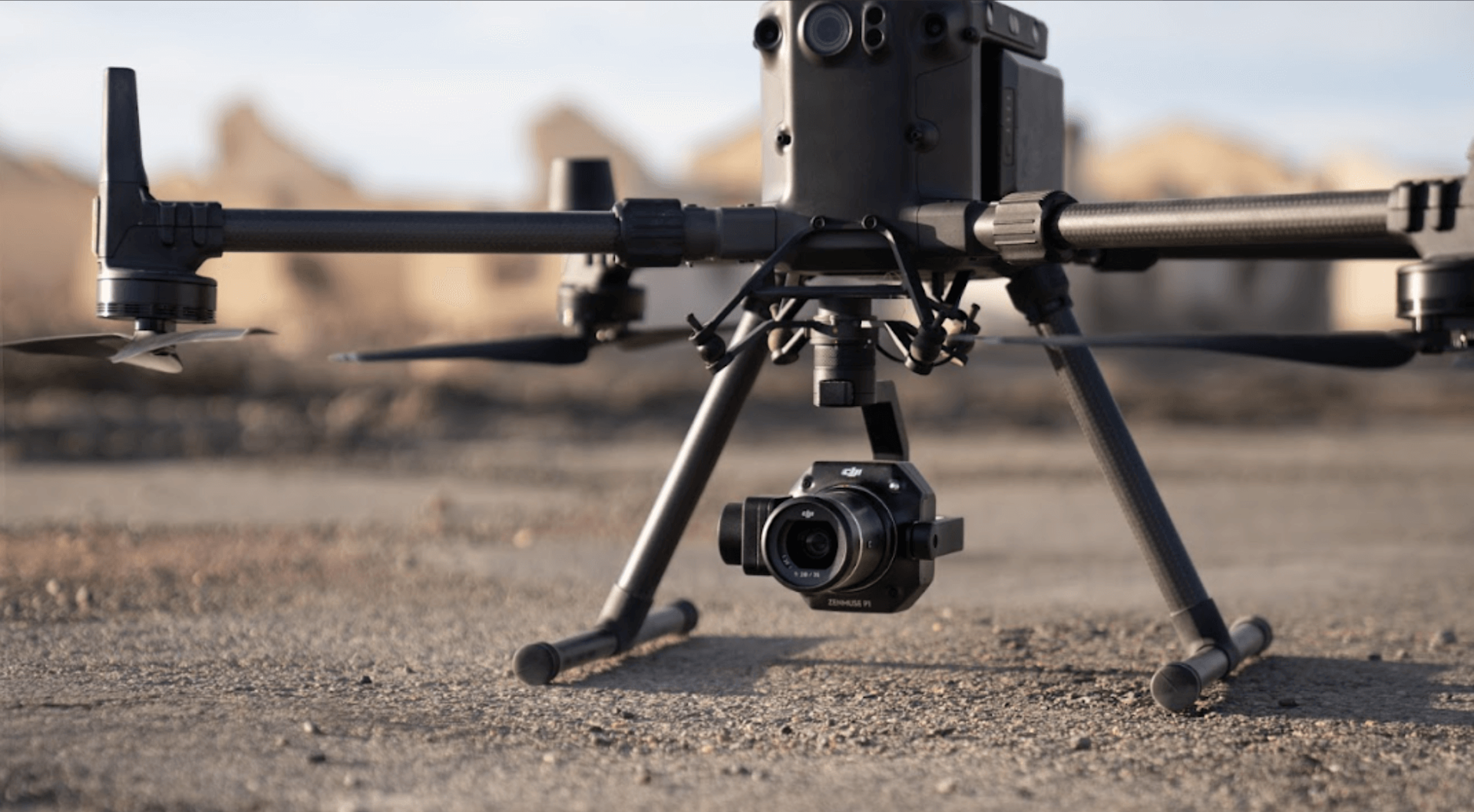

The P1 features Smart Oblique Capture. This function enables the single camera to function as all five of the cameras in an oblique camera system (ie, nadir, as well as front, back, left, and right).
When drawing the mapping area out on the DJI Pilot app (during mission planning), Smart Oblique Capture automatically divides the target surveying area into different sections. Sections in the centre of the surveying area get five photos, one at each angle (nadir, front, back, left, and right), while sections at the periphery of the surveying area require fewer photos.
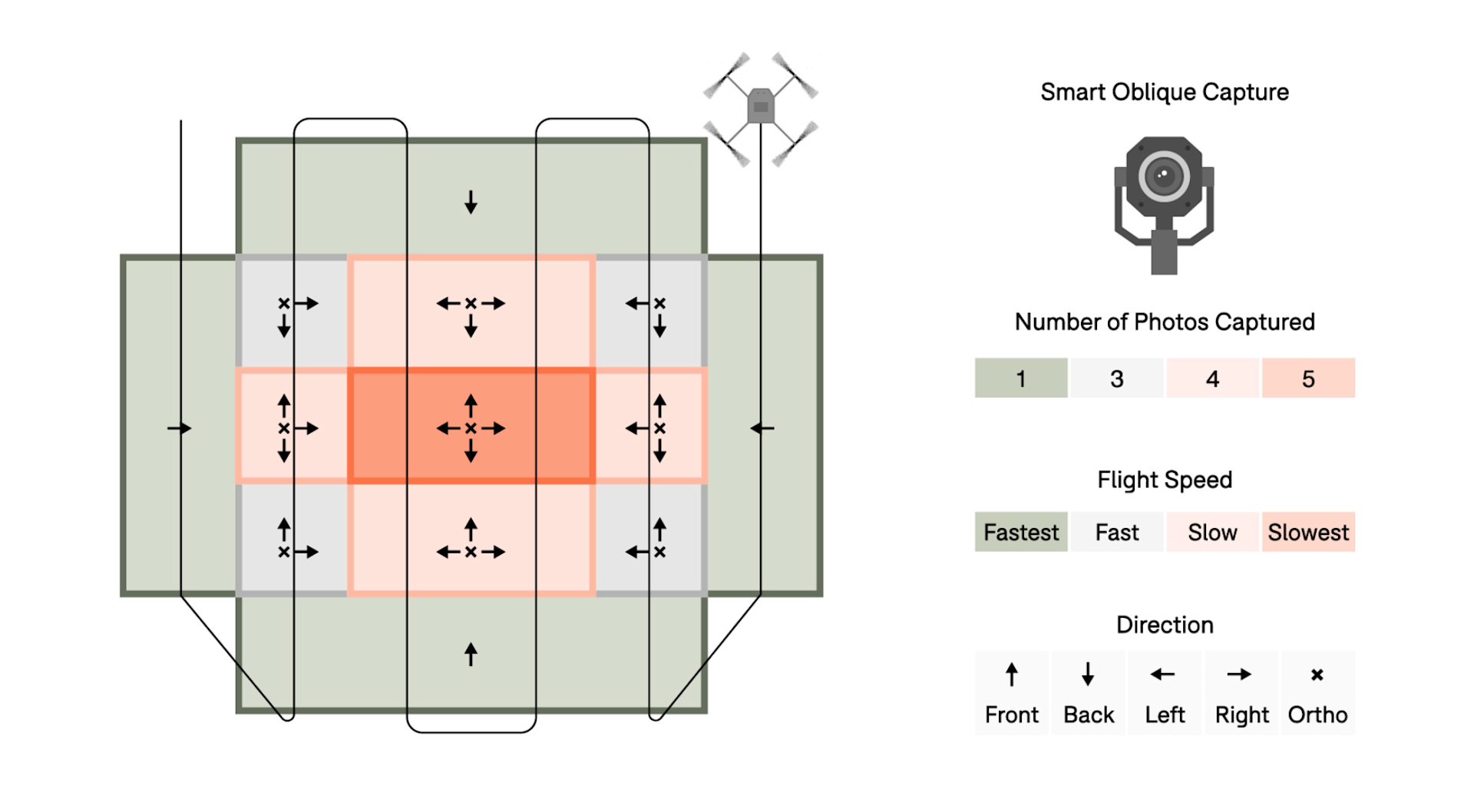
With Smart Oblique Capture, the position data, drone speed, and gimbal direction are embedded into the metadata of each photo in order to compensate for the shift in position and perspective; similar to the mathematical calculations used to amalgamate the consecutive captures in an oblique camera array.
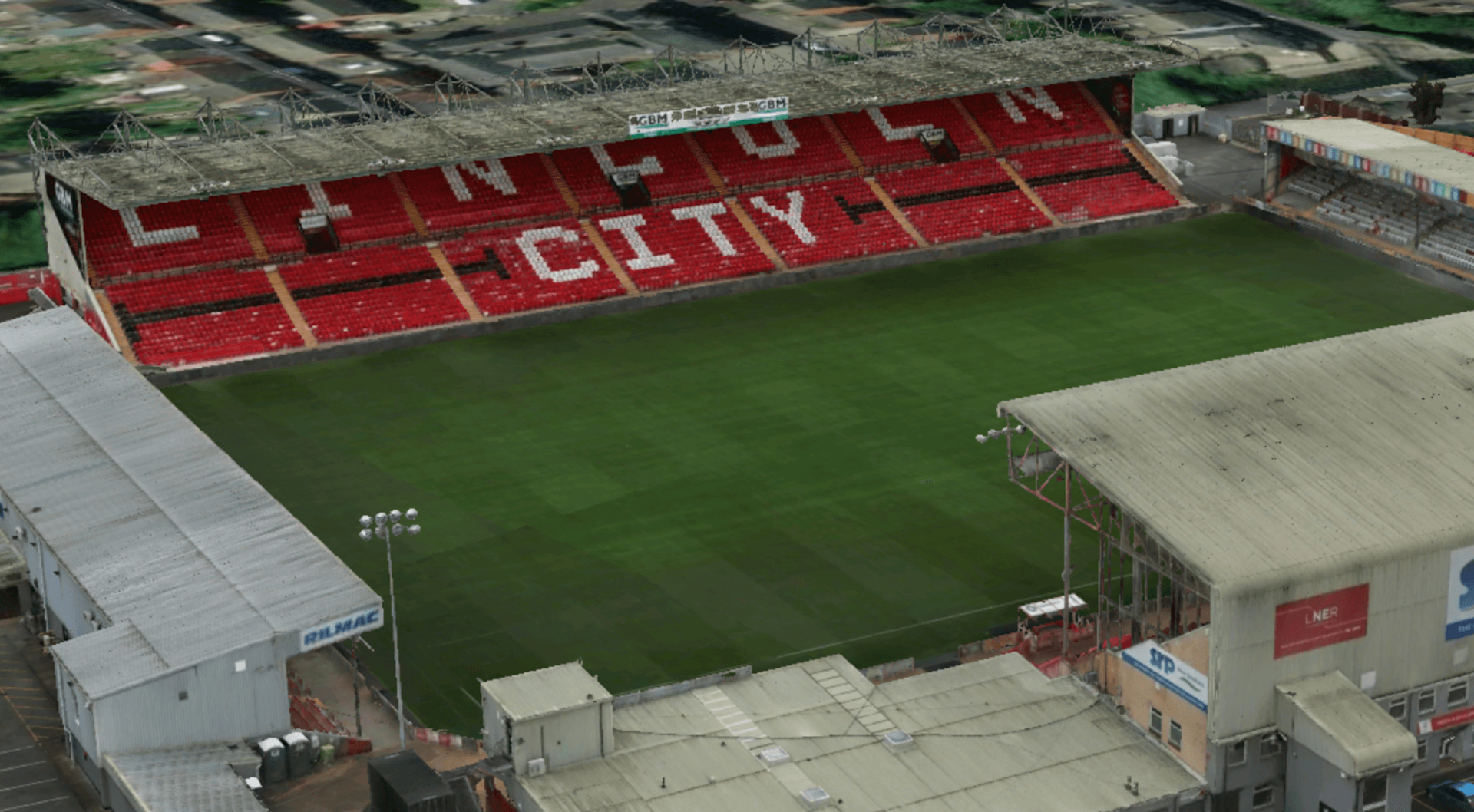
A 3D model, using data collected by the P1, is shown below.

DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise
The DJI Mavic 3 Enterprise is a lightweight, all-in-one drone surveying solution. This platform - ideal as an entry-level craft - has a 20MP 4/3 CMOS wide camera with a mechanical shutter, as well as a 12MP tele camera.

Like the DJI Zenmuse P1, the Mavic 3 Enterprise is capable of Smart Oblique Capture. A dataset from the Mavic 3 Enterprise is shown below.

Share UAV 203S Pro
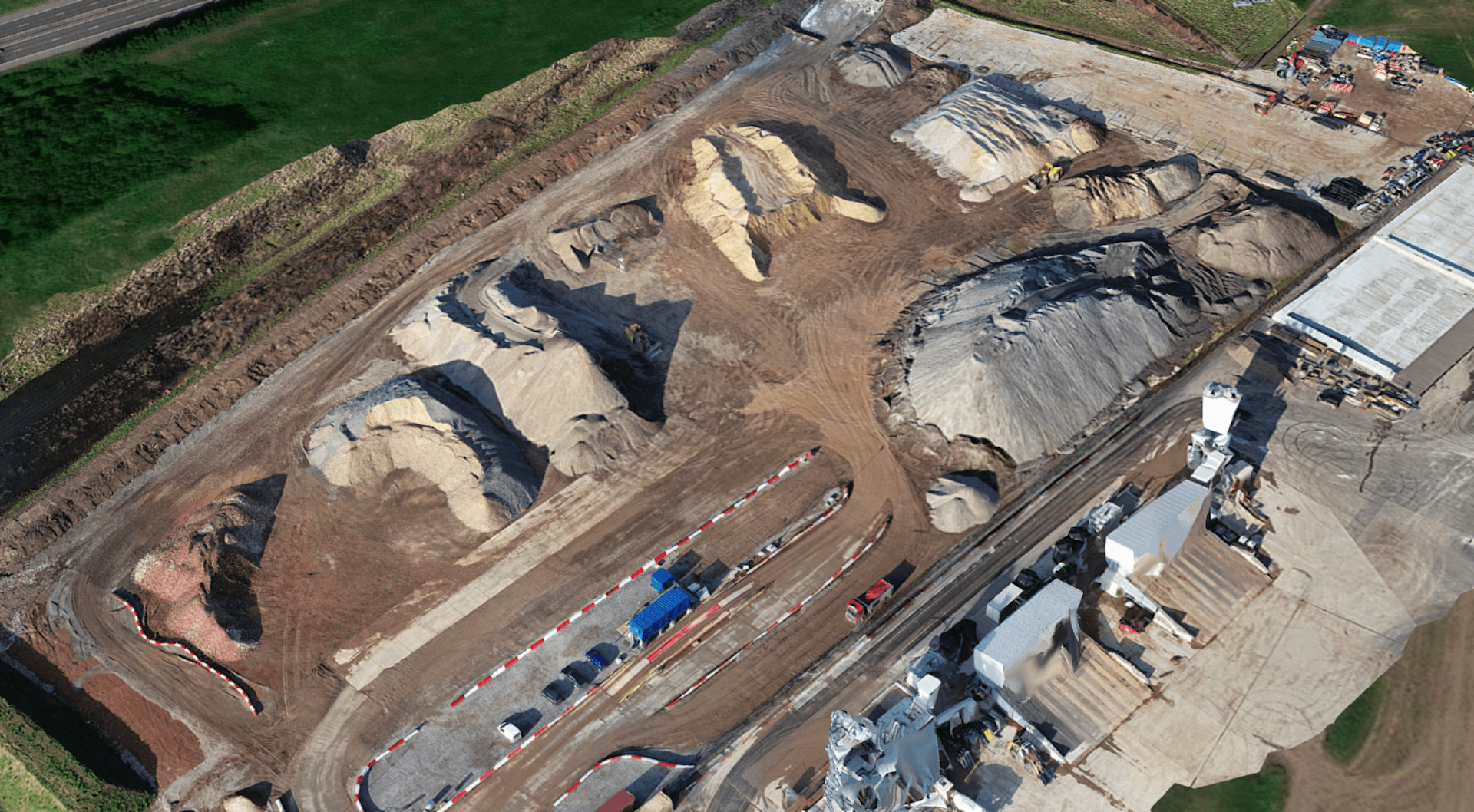
The Share UAV 203S Pro is a dedicated five-lens oblique mapping camera with a combined resolution of 225MP. Deploy it with the DJI M350 RTK or DJI M300 RTK.

Thanks to its five-lens array, it can capture nadir and oblique imagery during a single flight. Especially powerful for mapping larger sites, due to its increased efficiency, the Share 203S Pro is capable of producing highly-detailed 3D models, as this image below shows.

Share UAV PSDK 102S V3
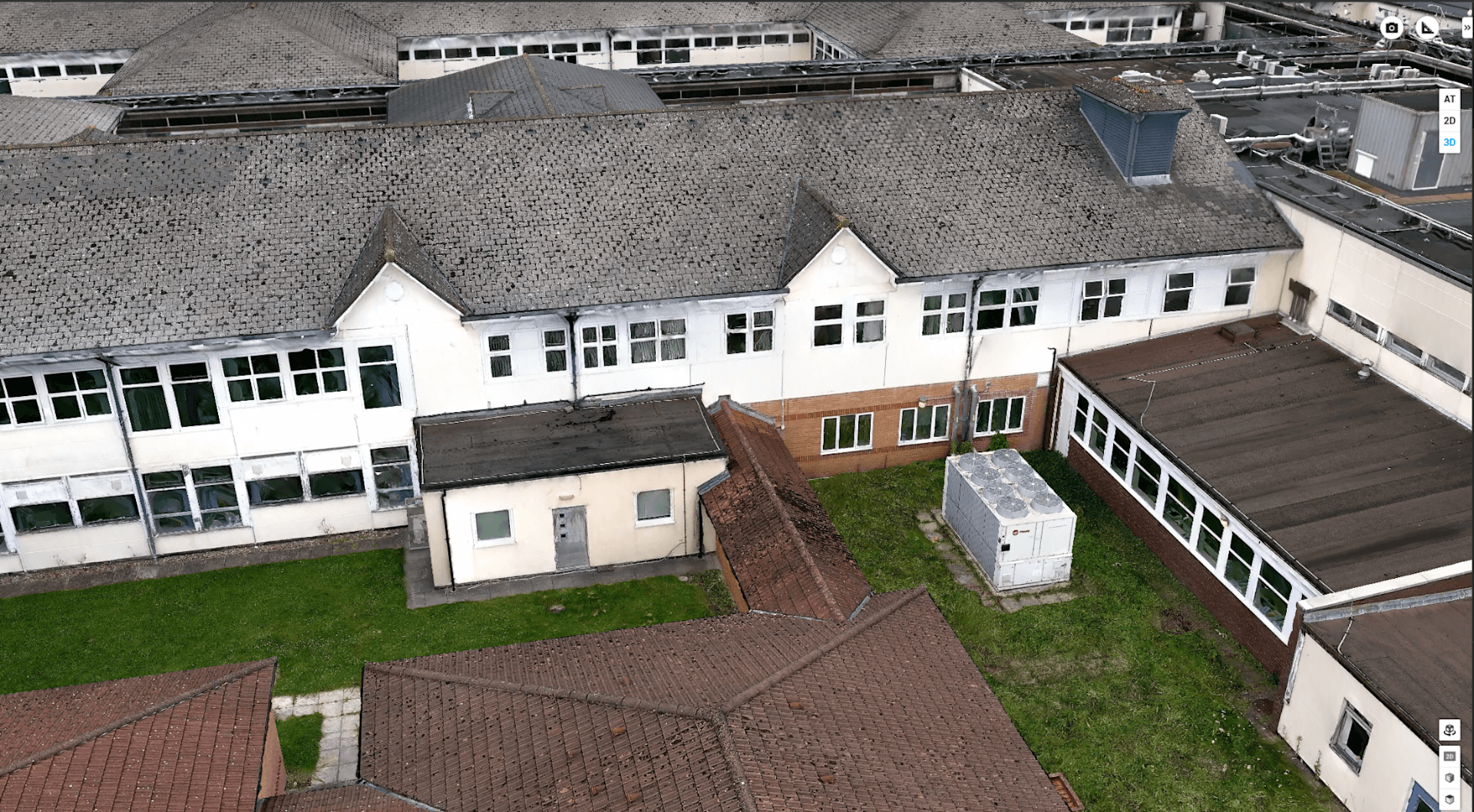
Like the Share UAV 203S Pro, the Share UAV PSDK 102S V3 is an oblique mapping camera with a five-lens array. Each camera has a resolution of 25.16MP.

It integrates with the DJI M300 Series and can capture all five angles (ie nadir, left, right, front, and back) during one flight.
An example dataset is shown below.

Summary
3D models have become a crucial go-to digital asset across a range of industry applications, and drones help streamline the data collection process.
As part of this, oblique imagery is a necessity - ensuring robust and accurate models.
And industry-leading solutions from DJI and Share UAV enable the ability to obtain quality and rapid oblique data to build reliable datasets.
To find out more about drone mapping and 3D modelling and to add any of these oblique survey solutions to your workflows, contact our enterprise specialists, including our in-house surveying department. Click to contact us.
