
Updated on 22 Oct 2024
DJI Dock 2: M3D vs M3TD - Which Drone Is Best For You?
Learn about the DJI Dock 2 drones, the DJI Matrice 3D & M3TD to help you determine the best option for drone operations.
The DJI Dock 2 is compatible with the new DJI Matrice 3D drone series;
DJI Matrice 3D engineered for high-precision surveying - making it DJI's first dedicated drone-in-a box solution for mapping;
DJI Matrice 3TD has thermal and RGB sensors, ideal for public safety, security, and inspection;
View data collected by heliguy™ to see the unique capabilities of each drone.
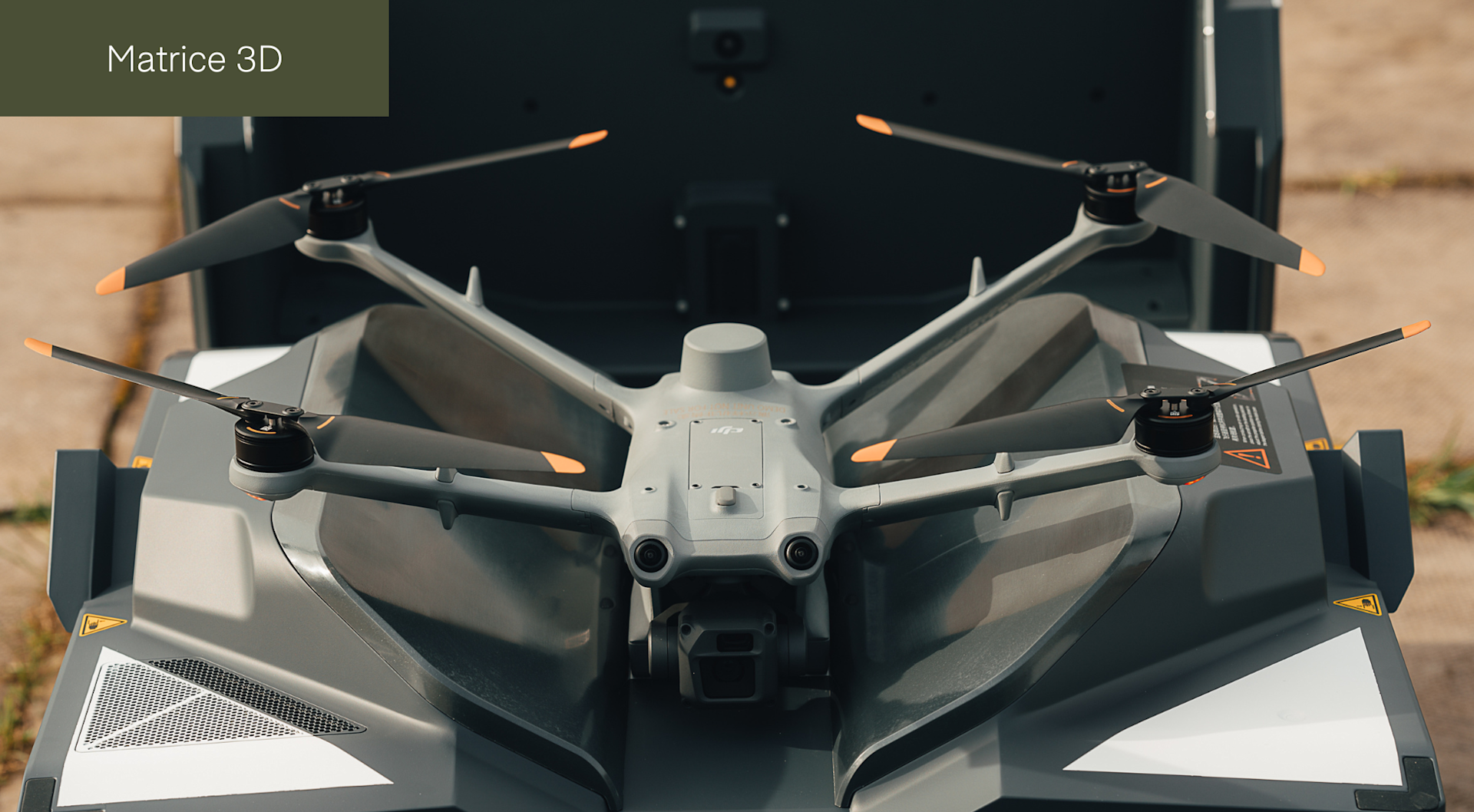
The DJI Dock 2 introduces two new drones: The DJI Matrice 3D and DJI Matrice 3TD.
Both aircraft are specifically designed for this docking station - which has a smaller footprint than the original DJI Dock, an IP55 rating, and is designed for remote and automated deployments.
Read our in-depth comparison between the Dock 2 and Dock 1 to learn about the differences between these two drone in a box solutions.
But which drone in the DJI Matrice 3D Series is best for you?

In short - it largely depends on your use case.
The M3D - equipped with a 4/3 CMOS 20MP sensor and mechanical shutter - is engineered for high-precision surveying, ideal for progress monitoring and earthworks calculations.
Meanwhile, the M3TD - featuring thermal and RGB sensors - is suitable for security, public safety, and inspection.
This blog highlights the key specifications of both drones and showcases datasets collected by heliguy™ to demonstrate their value in their ideal scenarios.
M3D vs M3DT: Key Specifications
Before we delve into the drones' key differences, ie their camera capabilities, we'll first provide an overview of their similarities.
Weight: 1410g
IP54 rating and -20°C to 45°C operating temperature.
50 minutes of maximum flight time.
10km maximum effective operating radius.
Six directional obstacle sensing system.
400 battery cycles.
Integrated RTK module: ±3cm positioning accuracy.
Fast-charge at DJI Dock 2: 32 minutes (20% to 90%).
Third-party payload support through E-port.
Both drones can be used for remote and automated deployments, collecting data on-demand.
M3D Vs M3TD: Camera Comparison
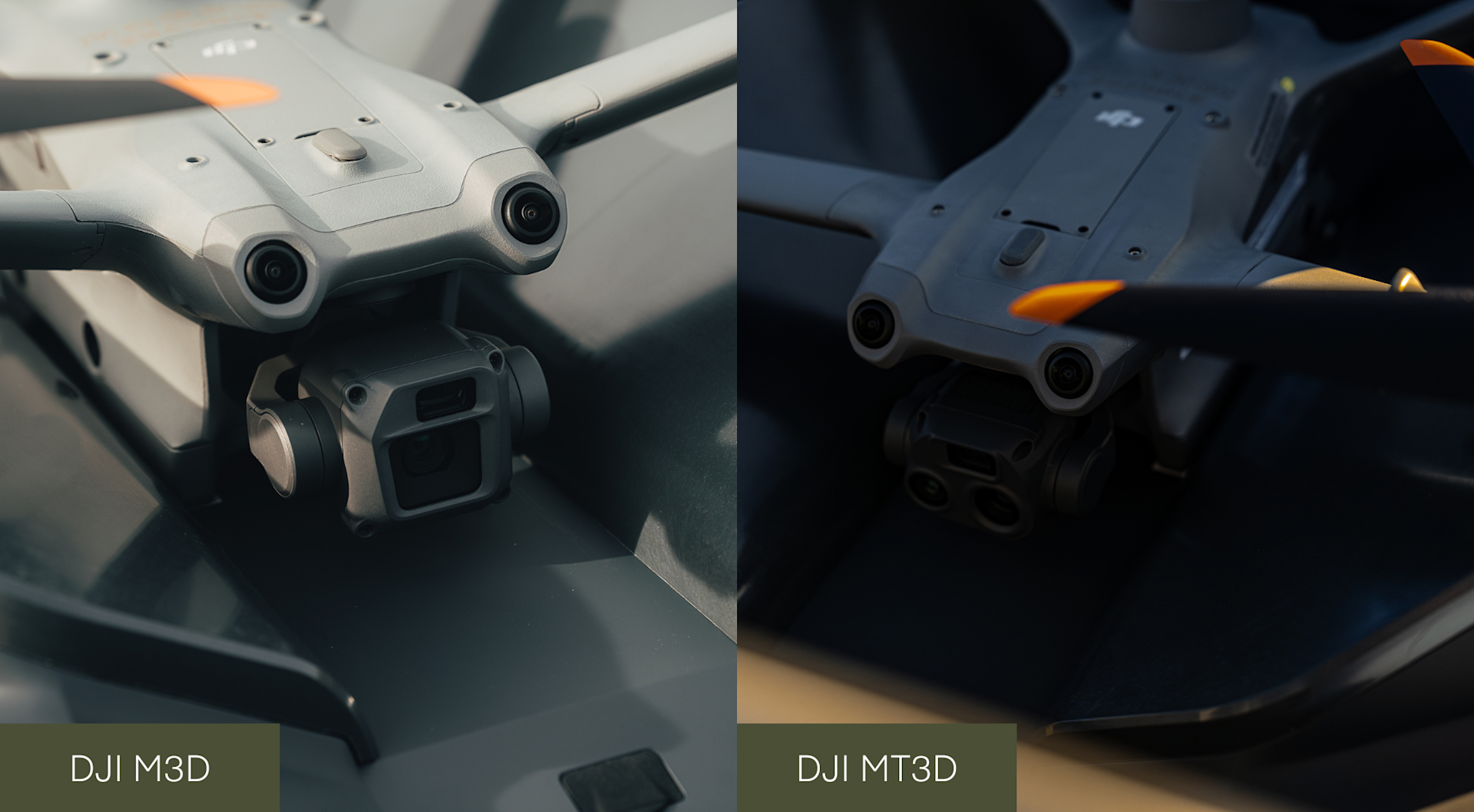
The key difference between the DJI M3D and DJI M3TD is their camera set-up.
DJI Matrice 3D is equipped with a tele camera and a wide-angle camera with a mechanical shutter, meeting the needs for 1:500 high-precision mapping tasks.

Meanwhile, DJI Matrice 3TD has RGB cameras (wide-angle and tele with zoom), and an infrared camera, enabling it to depict visible light and thermal images.
The table below provides an overview of the camera specifications for each platform.
DJI Matrice 3D | DJI Matrice 3TD | |
Wide-angle Camera | 4/3 CMOS 24mm Format Equivalent 20MP Effective Pixels Mechanical Shutter | 1/1.32-inch CMOS 24mm Format Equivalent 48MP Effective Pixels No mechanical shutter |
Tele Camera | 1/2-inch CMOS 162mm Format Equivalent 12MP Effective Pixels 56x hybrid zoom | 1/2-inch CMOS 162mm Format Equivalent 12MP Effective Pixels 56x hybrid zoom |
Thermal Camera | N/A | 40mm Format Equivalent Normal Mode: 640×512@30fps UHR Infrared Image Mode: 1280×1024@30fps (With the UHR Infrared Image function enabled, the aircraft automatically enables or disables UHR Infrared Image mode according to the ambient light brightness.) 28x Digital Zoom |
DJI M3D: Drone In A Box For High-precision Surveying
Thanks to its larger 4/3 CMOS 20MP camera with mechanical shutter and 0.7s shooting interval, the DJI M3D is engineered for high-precision surveying.
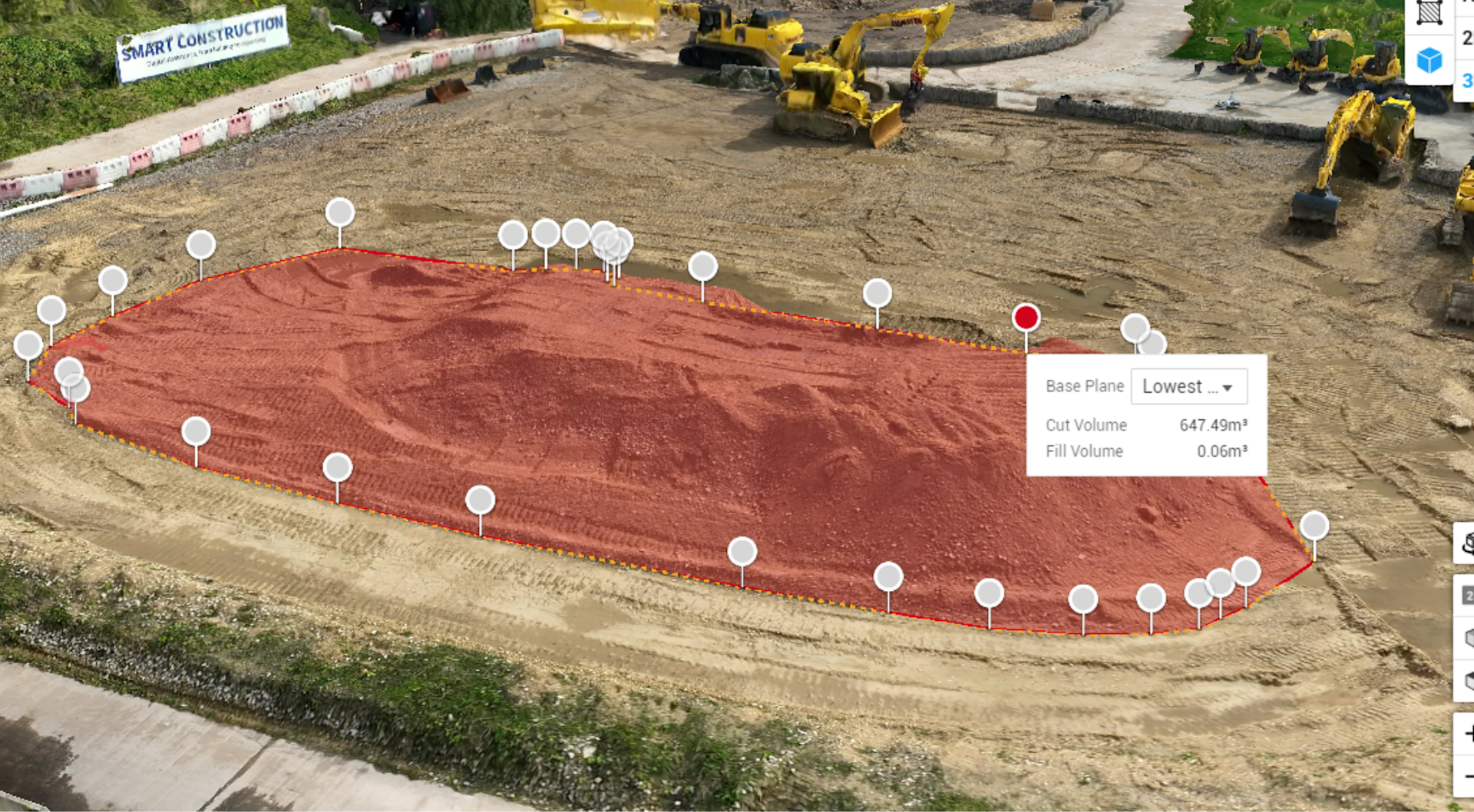
And with its ability to conduct remote and automated flights, the DJI Dock 2 can revolutionise construction workflows, remaining onsite to collect AEC information such as earthwork calculations or progress monitoring.
To test its capabilities, we planned a mission through DJI FlightHub 2. This mission was set up remotely and could be re-flown on demand for accurate and repeatable data collection.
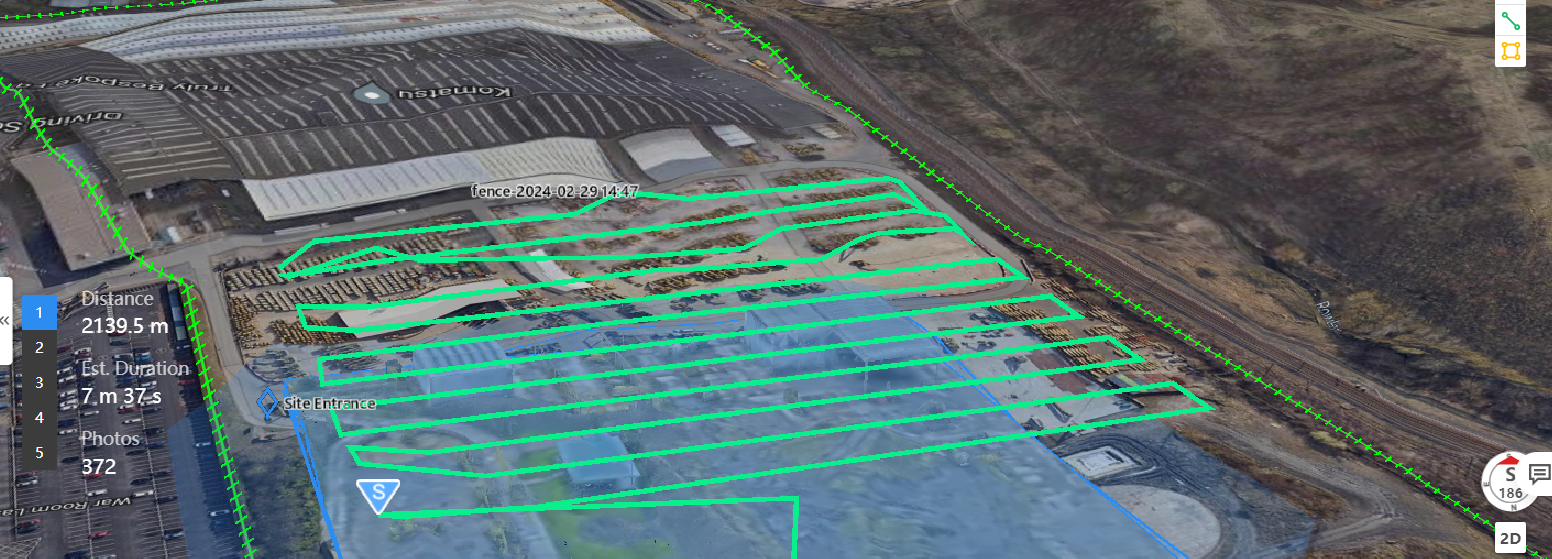
The mission has the following parametres:
Oblique flights (5 passes). 30m altitude. Overlap: 70% sideward, 80% forward.
GSD: 1.06cm.
Route planning based on high-precision 3D model which was overlaid in FlightHub 2. This provided an up-to-date map and accurate terrain/obstacle height information.
In this case, we conducted the operation with a visual observer on-site, who kept the drone in site during the mission and was ready to take control with the RC Plus Enterprise controller, if required.
The flight took 36 minutes, covering 0.026km², and collecting 1,853 images.
On arrival back at the Dock 2, the collected data was uploaded straight to the cloud, courtesy of the Cloud Mapping feature in DJI FlightHub 2.
The image below shows part of this model.
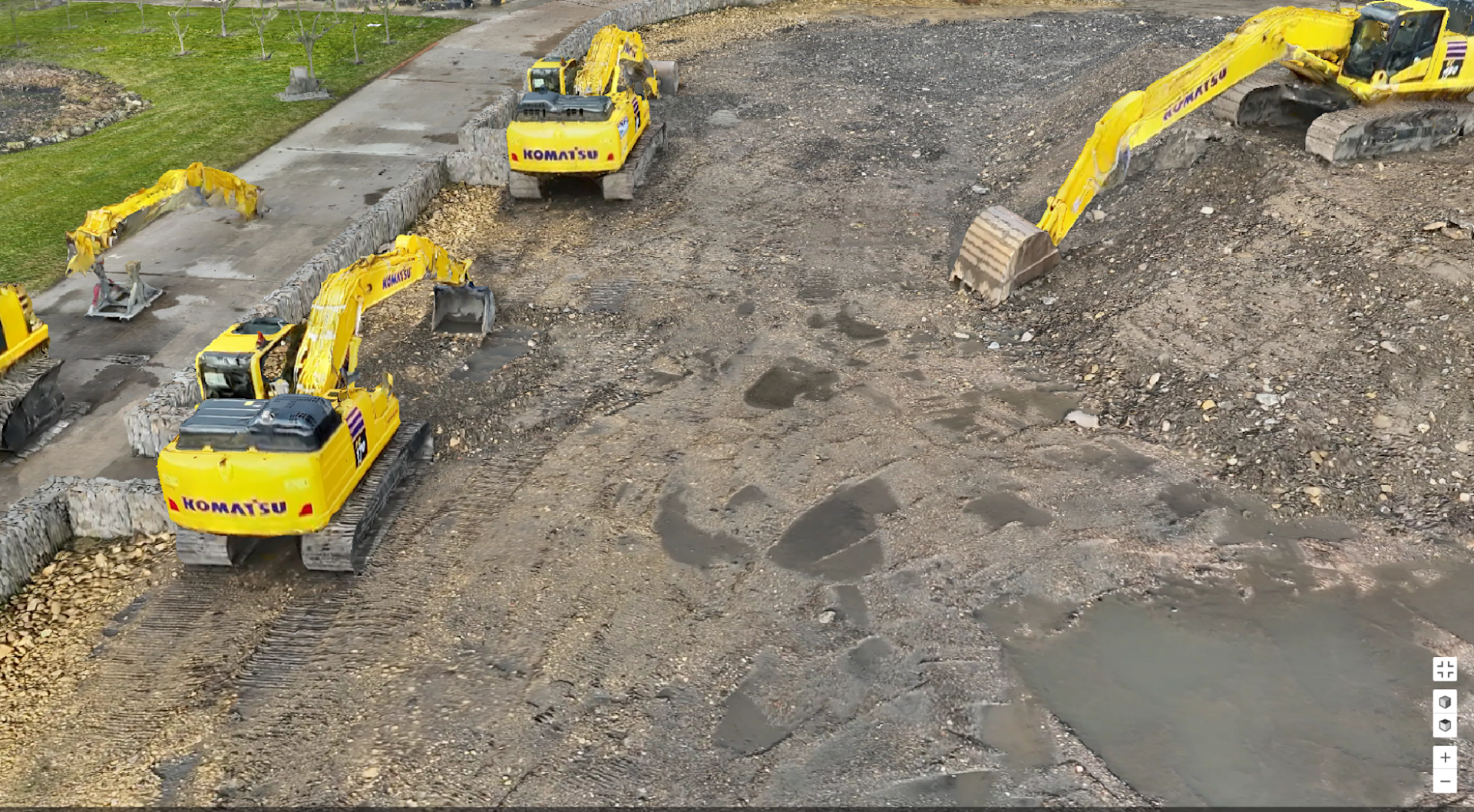

As well as the model, the real-world images can be viewed remotely through DJI FlightHub 2.
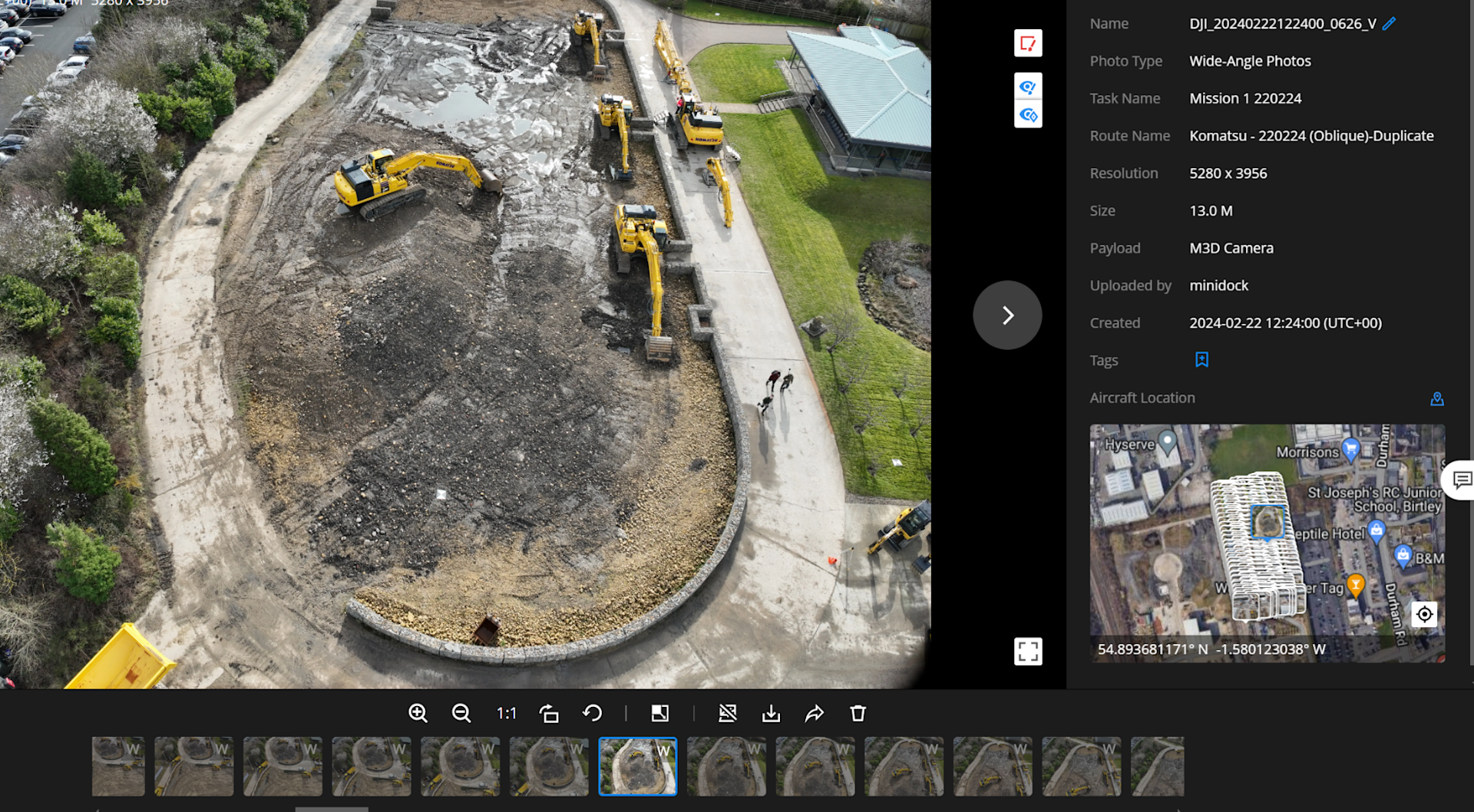
The data can then be uploaded to software, such as DJI Terra, to conduct anlaysis and calculations.

Other features of FlightHub 2 include a side-by-side model comparison to compare two images over time. This is useful for progress monitoring, for instance.

Meanwhile, DJI TerraAPI - which utilises cloud computing to achieve automated model reconstructions - is currently in a free trial stage.
heliguy™ has an in-house geospatial department that can offer drone surveying and data processing support, and help you integrate DJI Dock 2 into your workflows.
DJI M3TD: Thermal Drone In A Box Solution
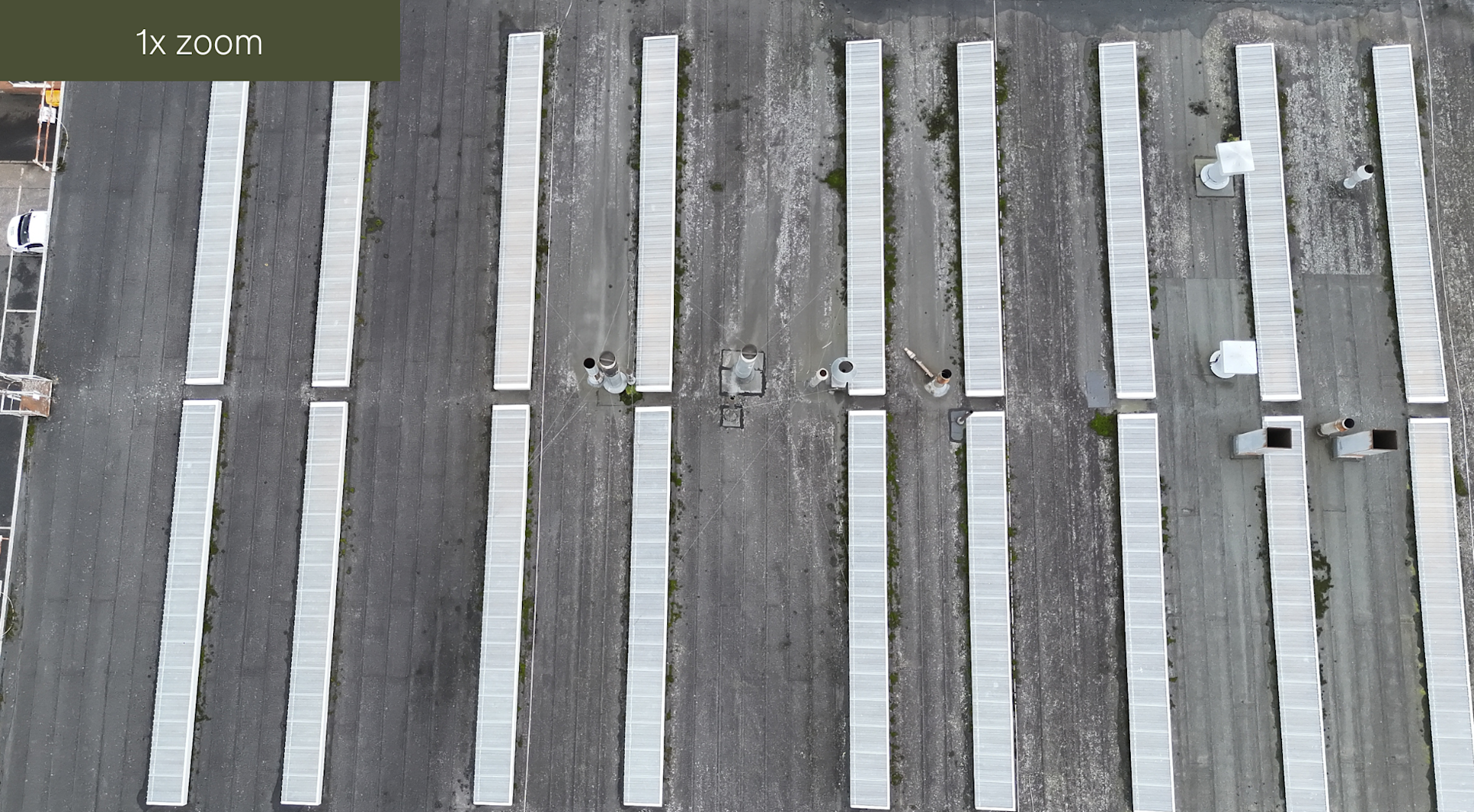
The DJI M3TD is more suited to inspection, public safety, and security tasks. This is thanks to its thermal and RGB payload array.
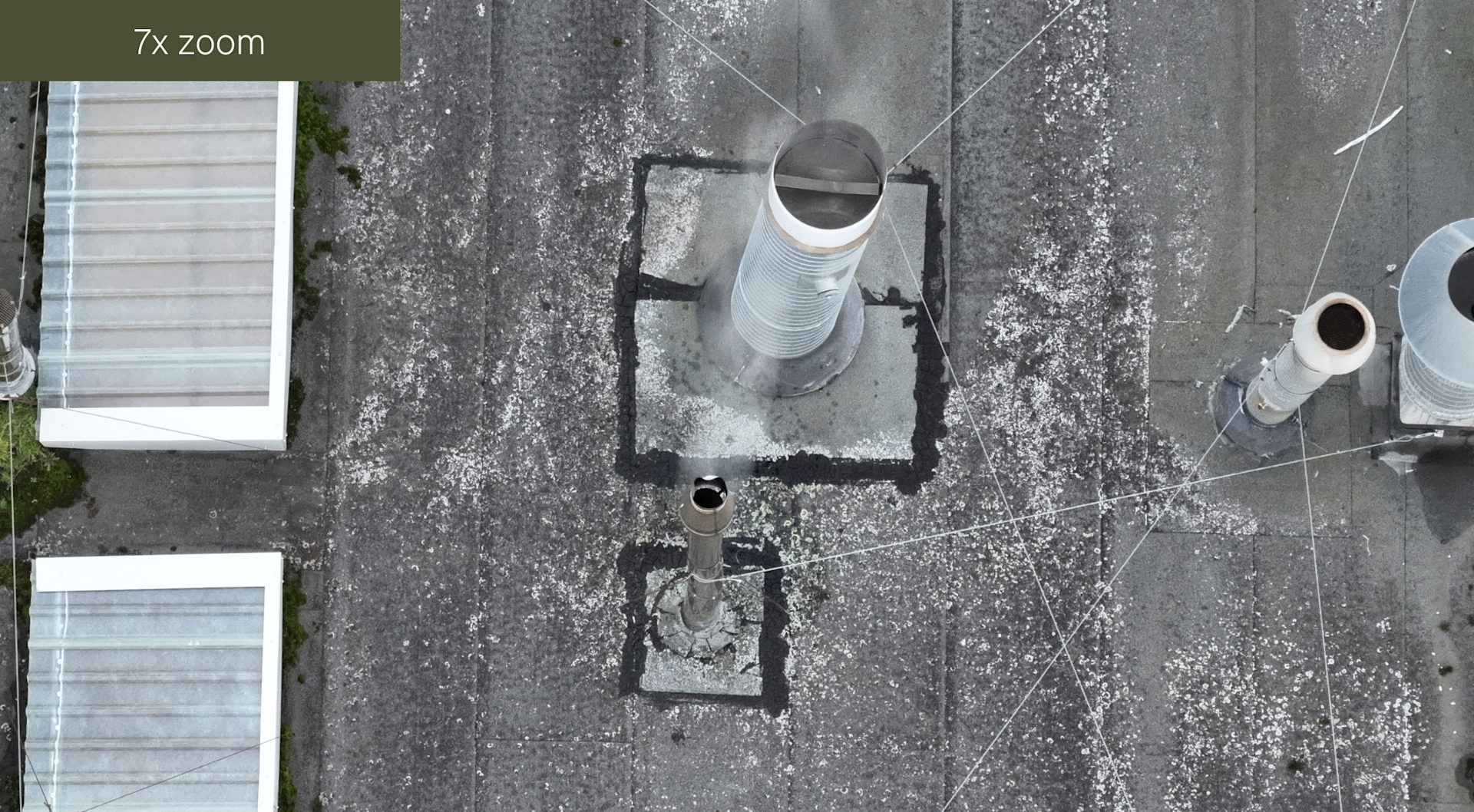
The capabilities of the DJI M3TD's sensor are demonstrated below, using imagery from a roof inspection.
Once again, we conducted an automated mission through DJI FlightHub 2, and ensured a visual observer was present during the flight.
We flew at 55m. We were able to set perimeters such as gimbal tilt.
This image shows how the thermal and RGB data from the roof inspection was viewed side-by-side.
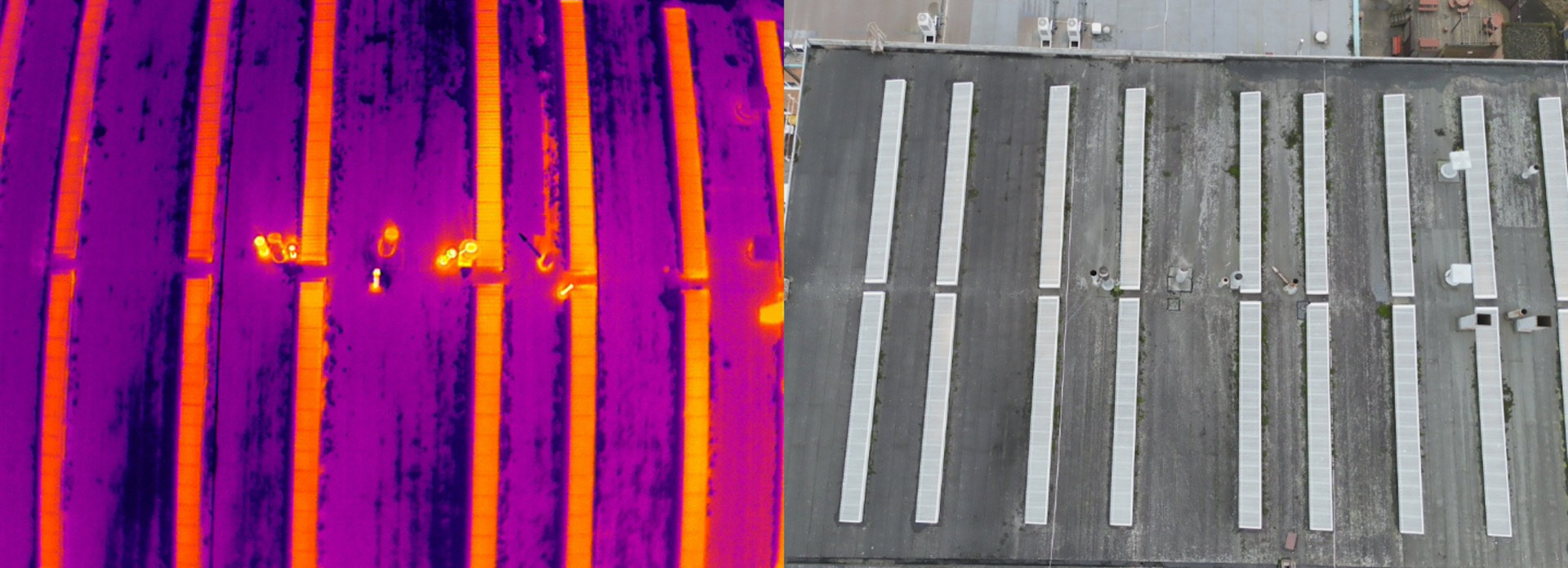
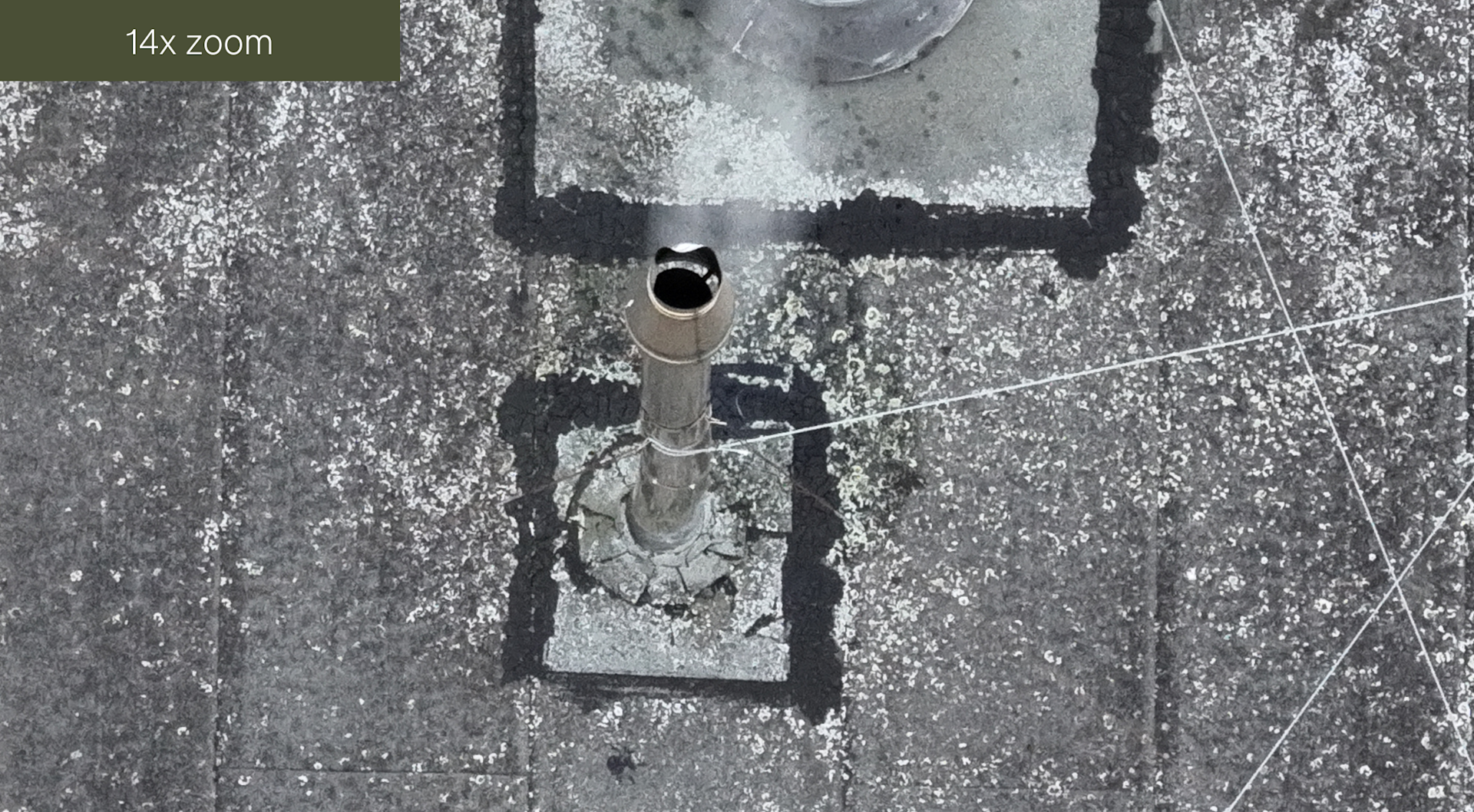
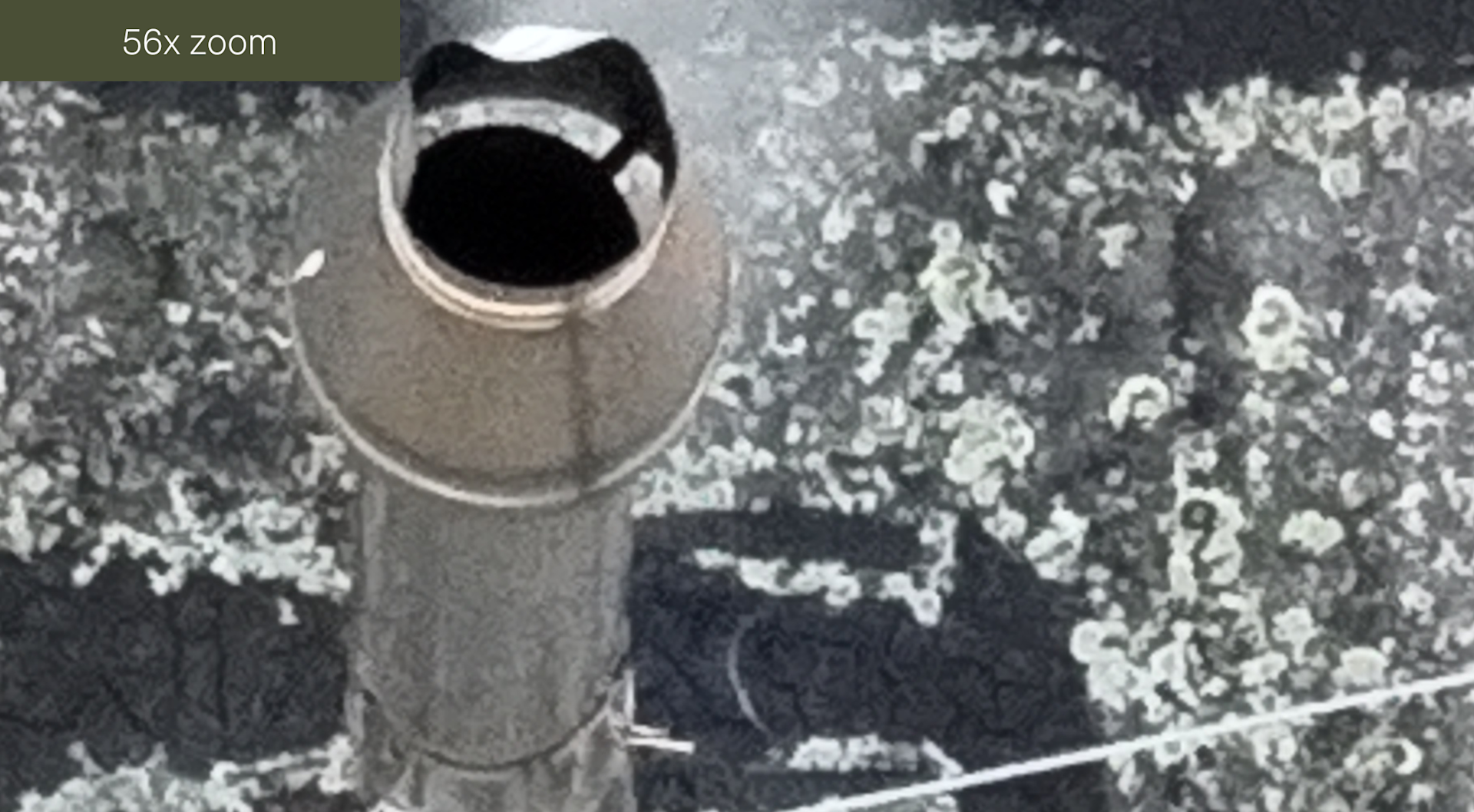
And these two images demonstrate the thermal zoom.
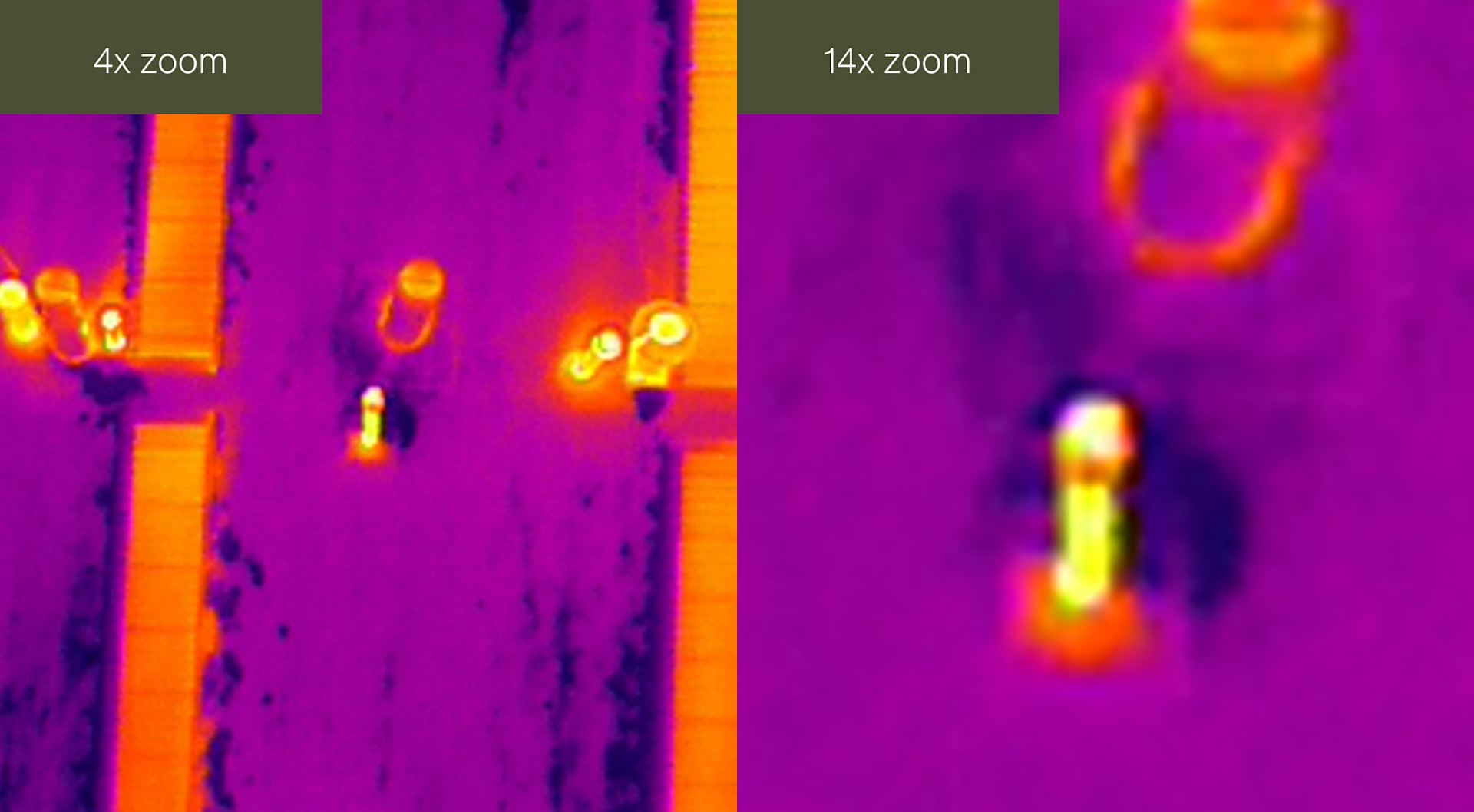

Meanwhile, this series of images demonstrate the zoom on the RGB camera.




The two images below - taken during the mission - show the flight screen within the DJI FlightHub 2 interface.
They demonstrate how the operation can be viewed remotely, featuring the flight path, the camera feed, and important information during the mission, such as battery life and wind speed.
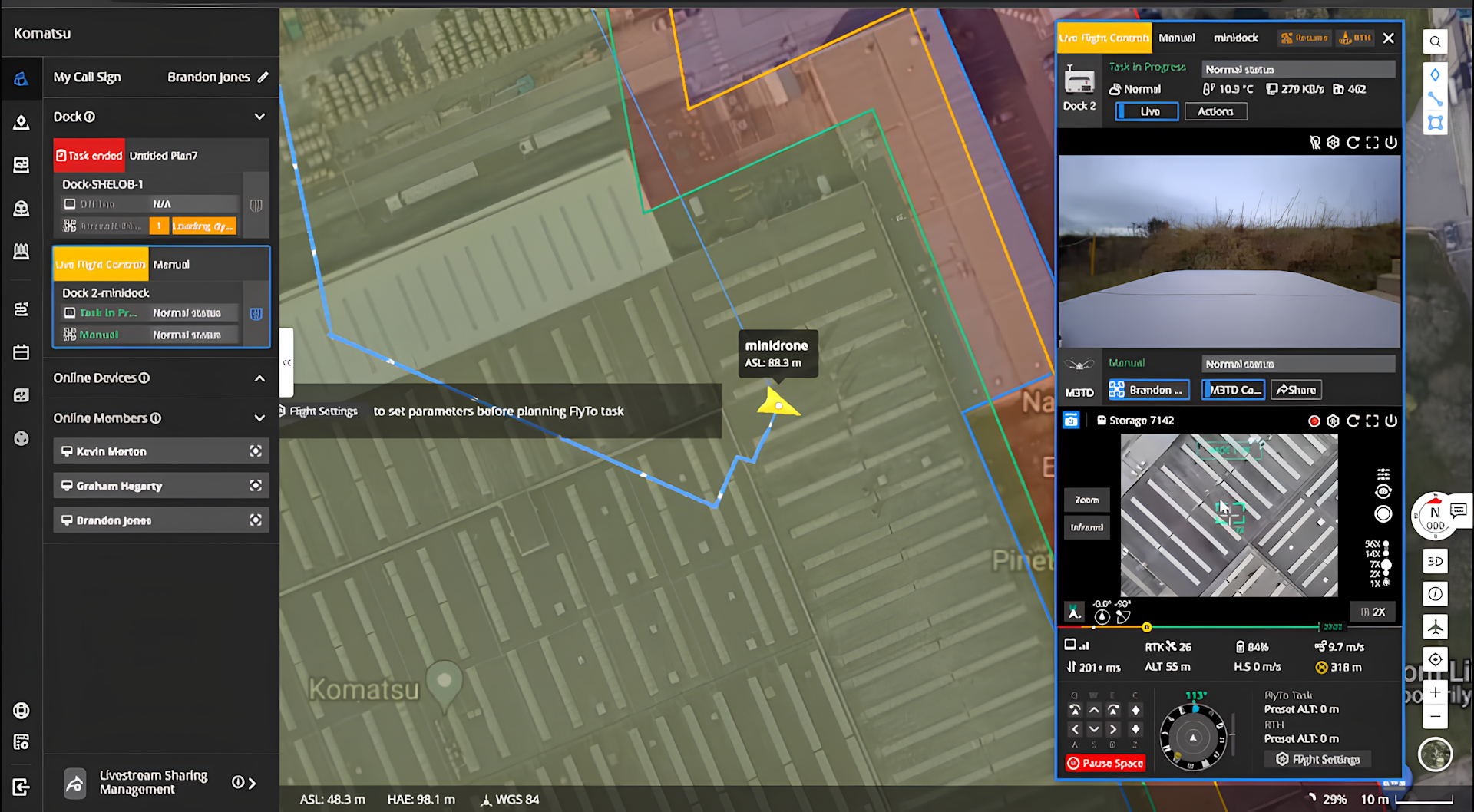
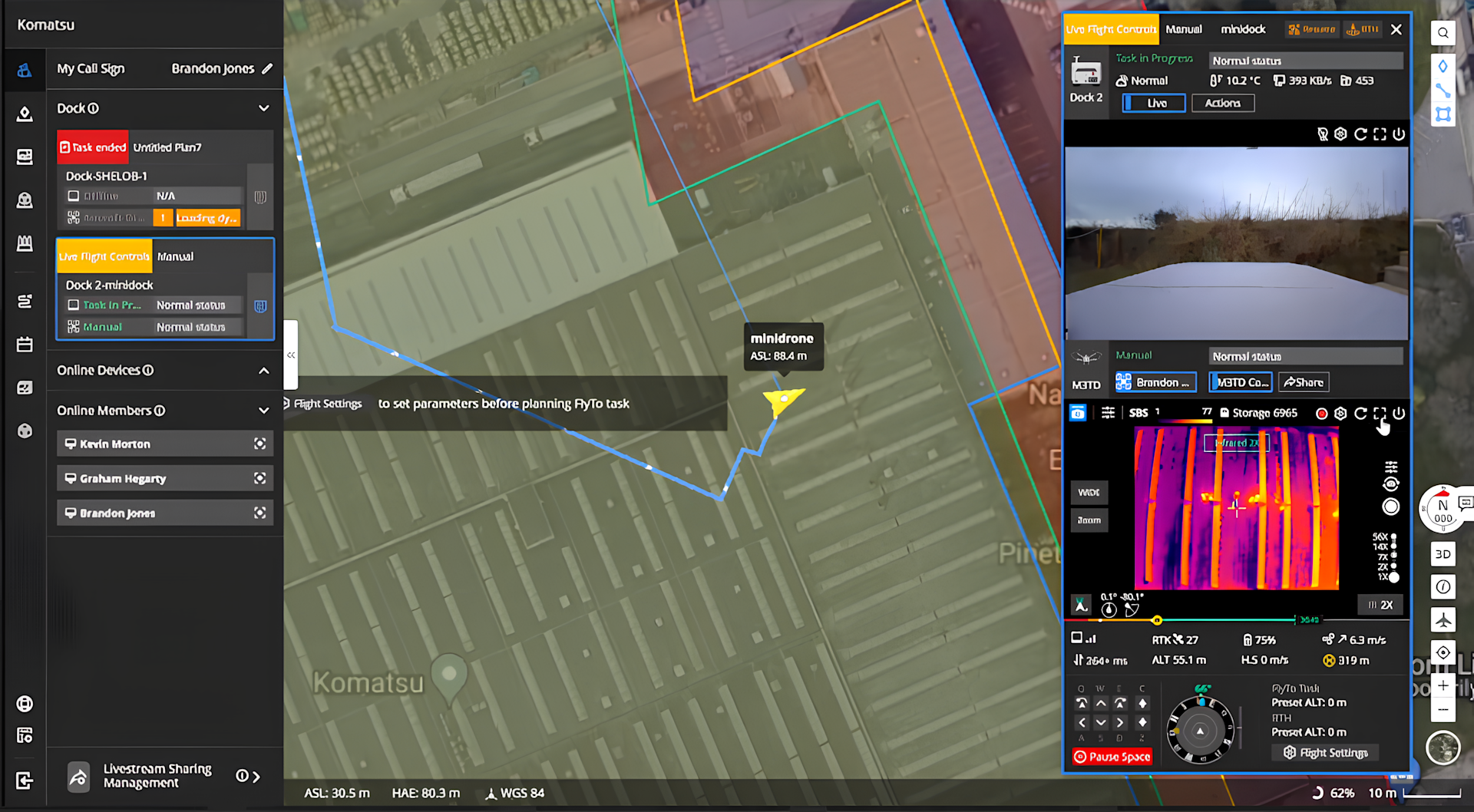
During the mission, we utilised FlightHub 2's Live Flight Control functionality. This enabled us to remotely take control of the payload and gimbal to adjust its camera to gain the required situational awareness. This included manually zooming on our areas of interest.
The mission could also be live streamed through FlightHub 2: Ideal for sharing the real-time view through the internet to anyone in the world.
Upon landing, the images were automatically uploaded for further analysis.
DJI M3D Vs DJI M3TD: Summary
The DJI Matrice 3D Series are rugged, robust, and high-class performers.
Working in conjunction with the DJI Dock 2, they are designed to empower automated and remote operations.
Which solution you choose largely depends on your requirements.
DJI M3D represents DJI's first surveying drone in a box solution, making it ideal for jobsites where earthwork calculations and progress monitoring are required.
Meanwhile, DJI M3TD offers a drone-in-a-box solution for inspection, public safety, and security operations, thanks to its built-in RGB, thermal, and zoom sensor array.
heliguy™ is a DJI Dock 2 partner and can help you integrate it into your workflows. This includes site planning, maintenance, survey support, training, and OSC consultancy for BVLOS operations. Contact us to find out more.

written by
James Willoughby
James joined heliguy™ in 2018 following a 13-year stint in print and online journalism, having worked on regional and weekly newspaper titles. He is responsible for spearheading heliguy™'s content strategy and social media delivery. James collaborates with DJI Enterprise's European marketing team to coordinate and produce case studies and helps organise events and webinars.