
Updated on 12 Dec 2024
SLAM vs GNSS For LiDAR Surveying
Comparison between SLAM and GNSS for LiDAR surveying.
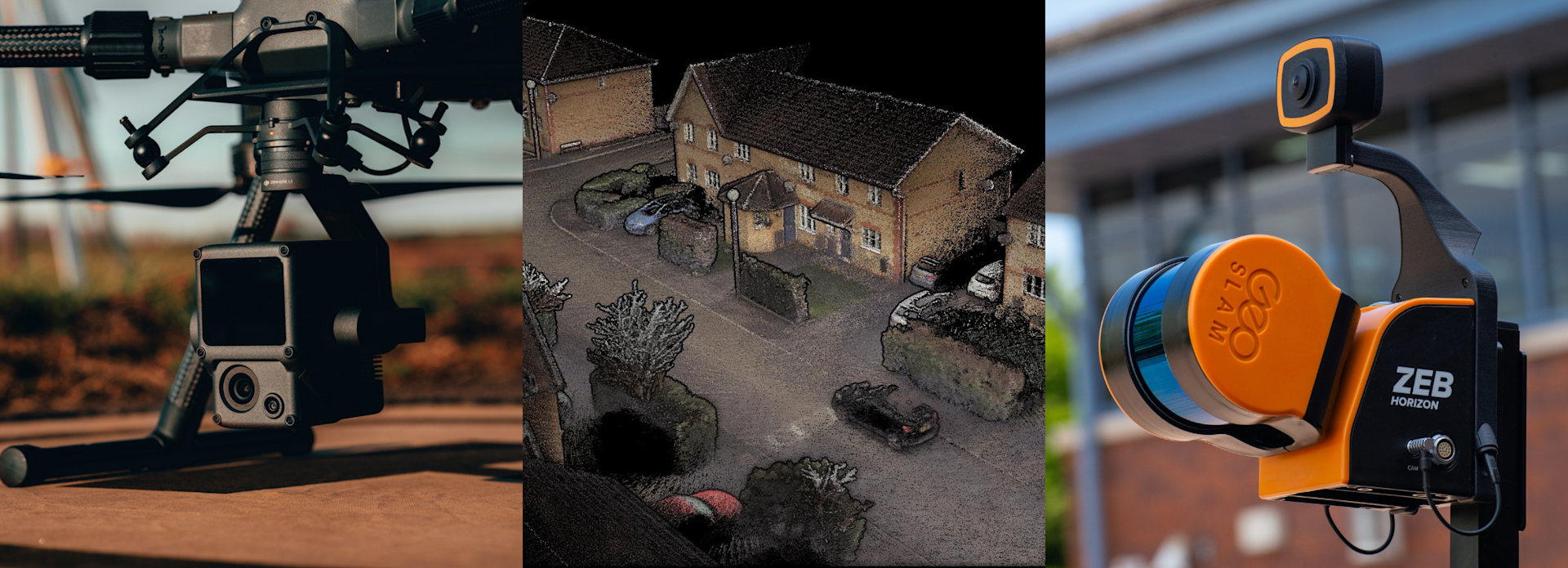

In-depth comparison between SLAM-based and GNSS LiDAR techniques for surveying;
The key advantages of SLAM include its ability for rapid mobile mapping, especially in areas where GNSS signal is limited or not available;
Generally speaking, GNSS LiDAR surveying is a more streamlined and efficient solution for natively achieving accurate absolute positioning data;
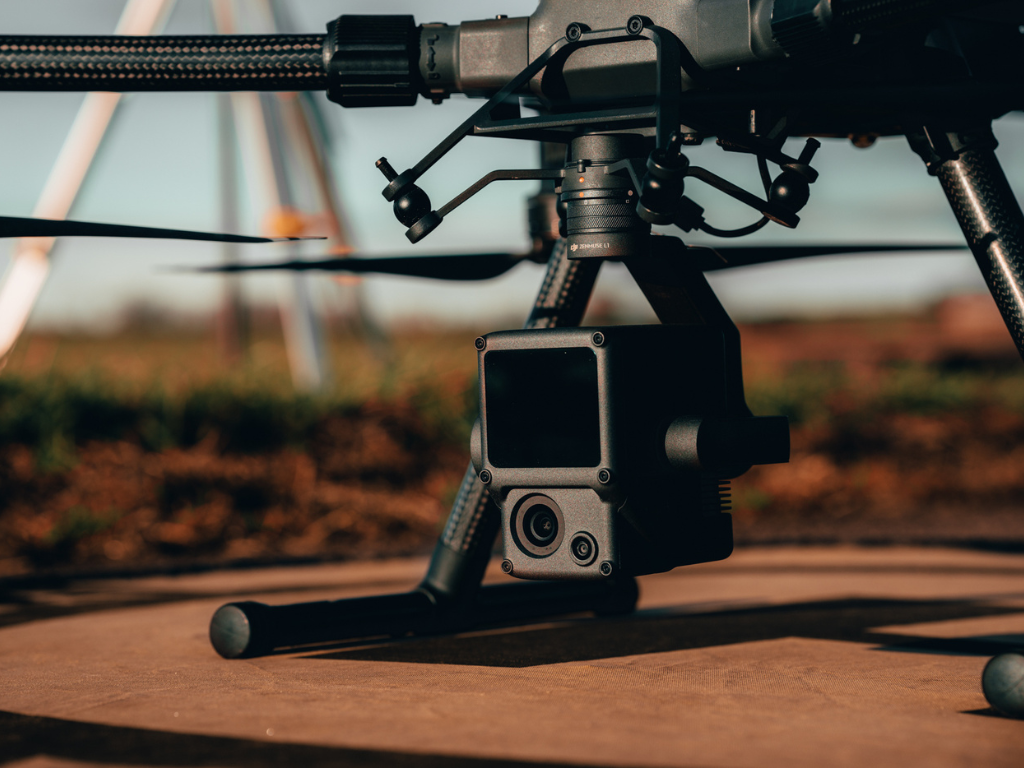
The heliguy™ surveying ecosystem includes SLAM and GNSS LiDAR solutions, such as hardware from GeoSLAM and the DJI Zenmuse L1.
LiDAR surveying has transformed the way that detailed 3D data is captured for mapping, construction, and environmental applications.
In the realm of LiDAR surveying, two prominent methods of positioning have emerged: Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM) and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS).
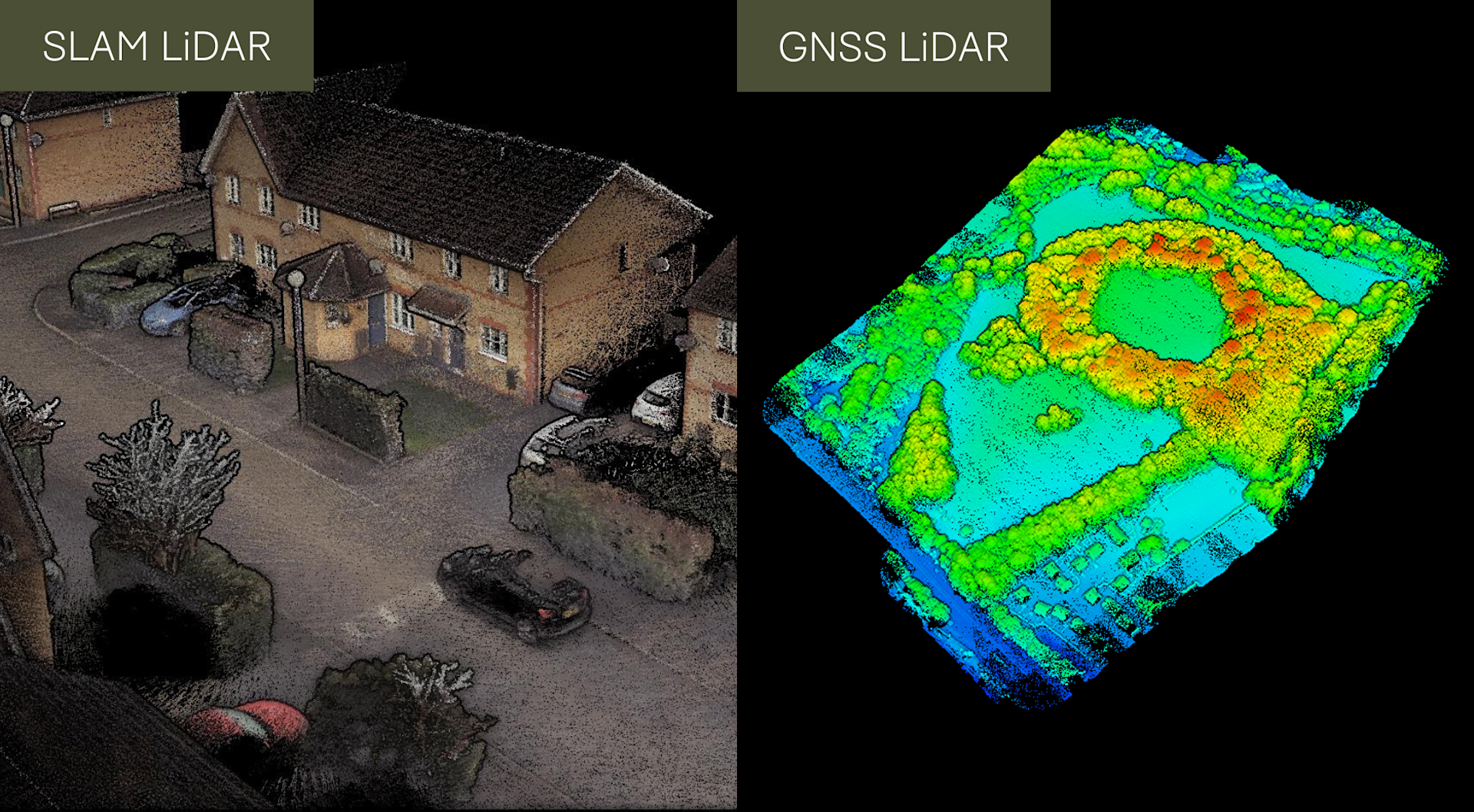
heliguy™'s surveying ecosystem consists of solutions for both of these techniques: For instance, the DJI Zenmuse L1 utilises GNSS, while the GeoSLAM range of sensors, including the ZEB Horizon, are SLAM-based.
In this blog, we will compare SLAM and GNSS techniques for LiDAR surveying, focusing on their applications, and respective strengths and weaknesses.
What Is The Difference Between SLAM And GNSS For Surveying?
SLAM technology enables surveyors to create accurate maps while simultaneously determining their position within the mapped environment.
It utilises a combination of sensors, such as LiDAR, cameras, and inertial measurement units (IMUs), as well as complex algorithms, to gather data and build detailed maps with localisation information.
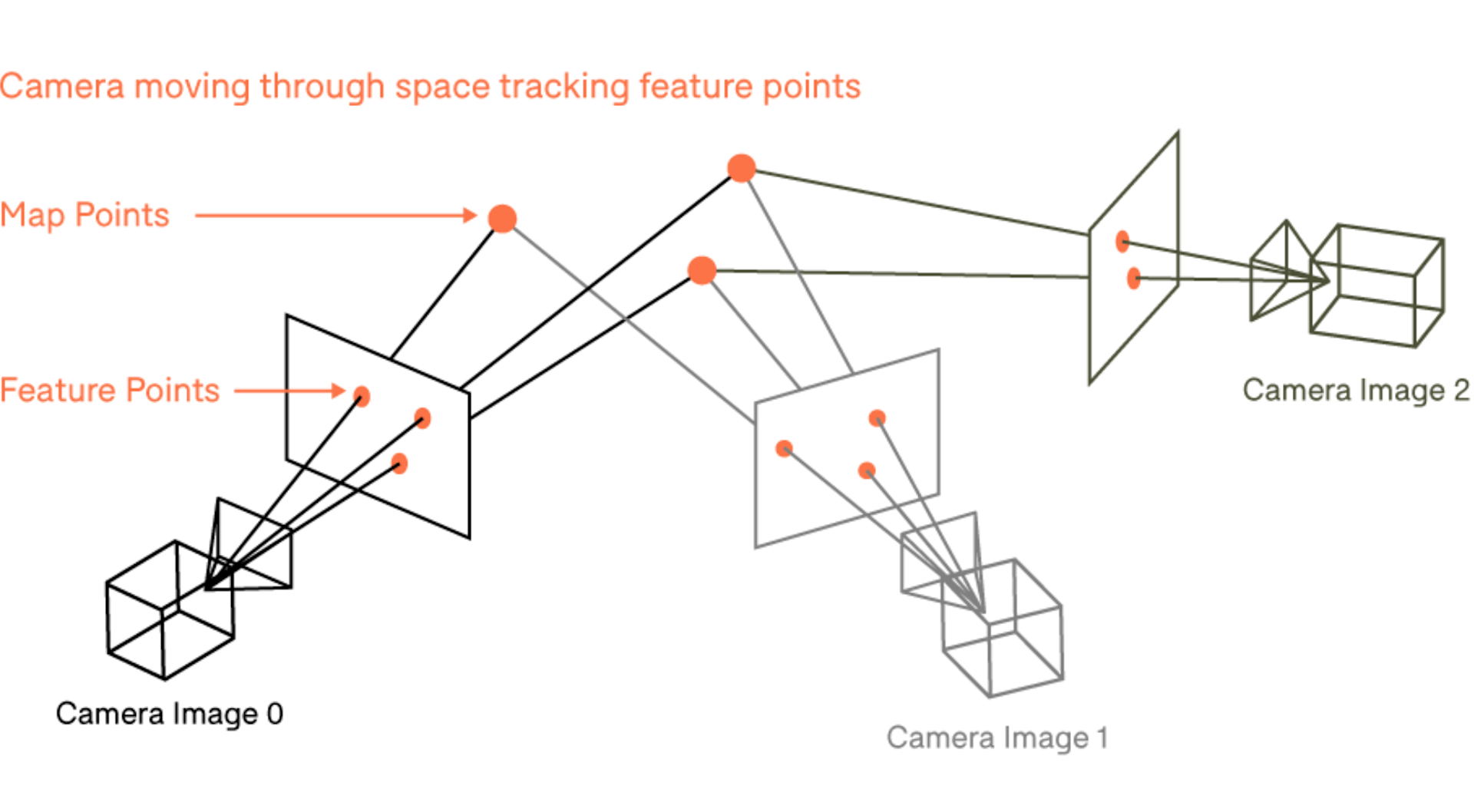
SLAM algorithms continually update and refine the map as the surveyor moves through the area, ensuring real-time mapping capabilities.
In contrast, GNSS technology provides precise positioning information by utilising signals from satellite constellations such as GPS, GLONASS, or Galileo.
In LiDAR surveying, GNSS is used to determine the absolute position of the LiDAR sensor and to georeference the acquired data accurately - offering precise mapping, absolute positioning, and elevation information.
SLAM Vs GNSS: Advantages For Surveying
SLAM and GNSS have their own distinct advantages for surveyors.
SLAM LiDAR Scanning: Surveying Benefits And Applications
1: Real-time mapping and localisation
SLAM enables surveyors to obtain accurate, up-to-date maps while simultaneously determining their precise location within the surveyed area.
It provides the ability to create maps on the fly, making it ideal for applications that require real-time data acquisition and mapping.
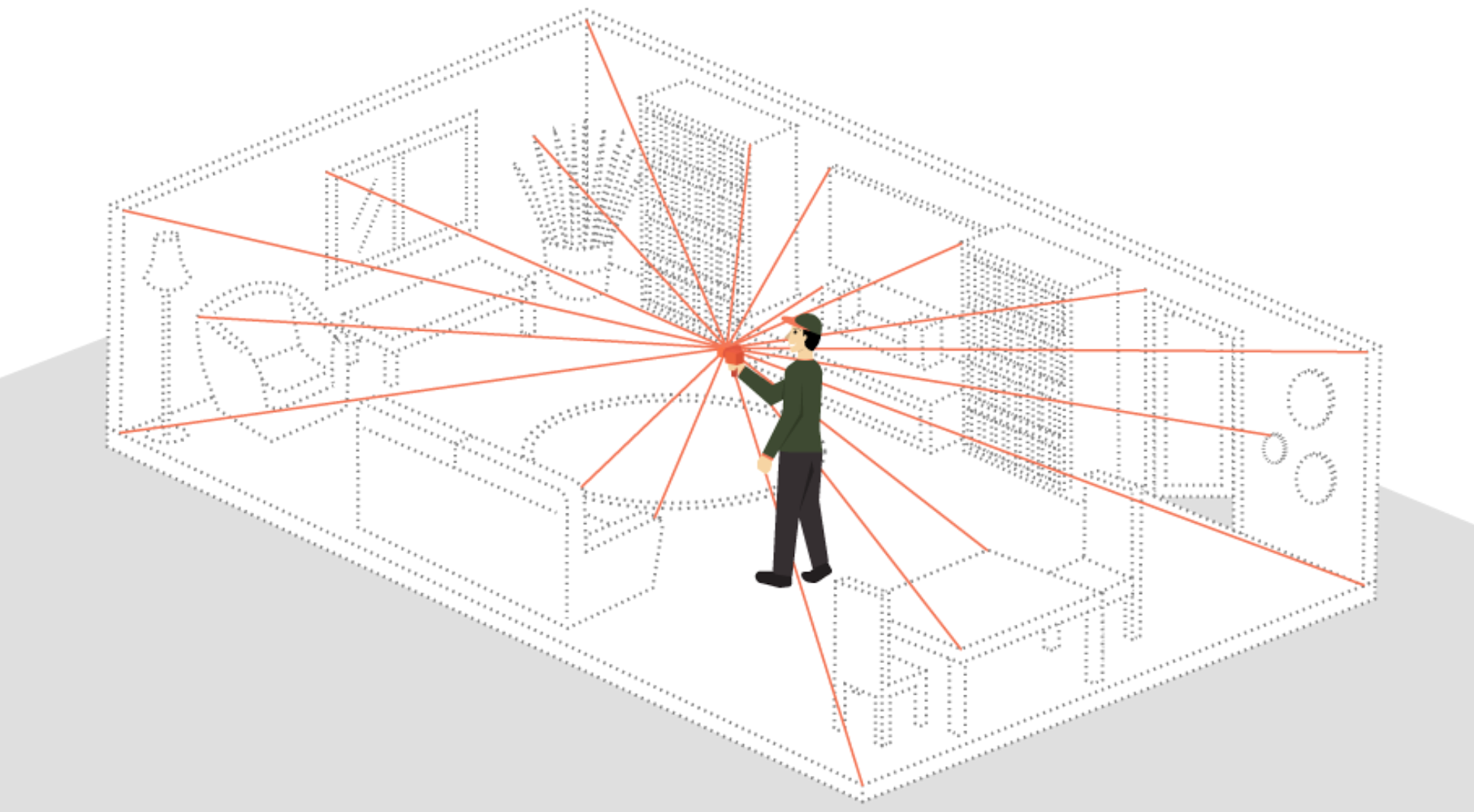
2: Flexibility in indoor and GPS-denied environments
SLAM is particularly useful for indoor surveys and GPS-denied areas, where GNSS signals may be weak or unavailable.
This is particularly beneficial when conducting surveys in underground mines, urban environments with high-rise buildings, and forests where tree canopies can be a hindrance for signal.
For instance, this video shows how GeoSLAM hardware was used to scan an underground tunnel network.
The resulting point cloud was used to detect the speed of change of rock movement, which can be a critical indicator of potential slope/rockface instability.
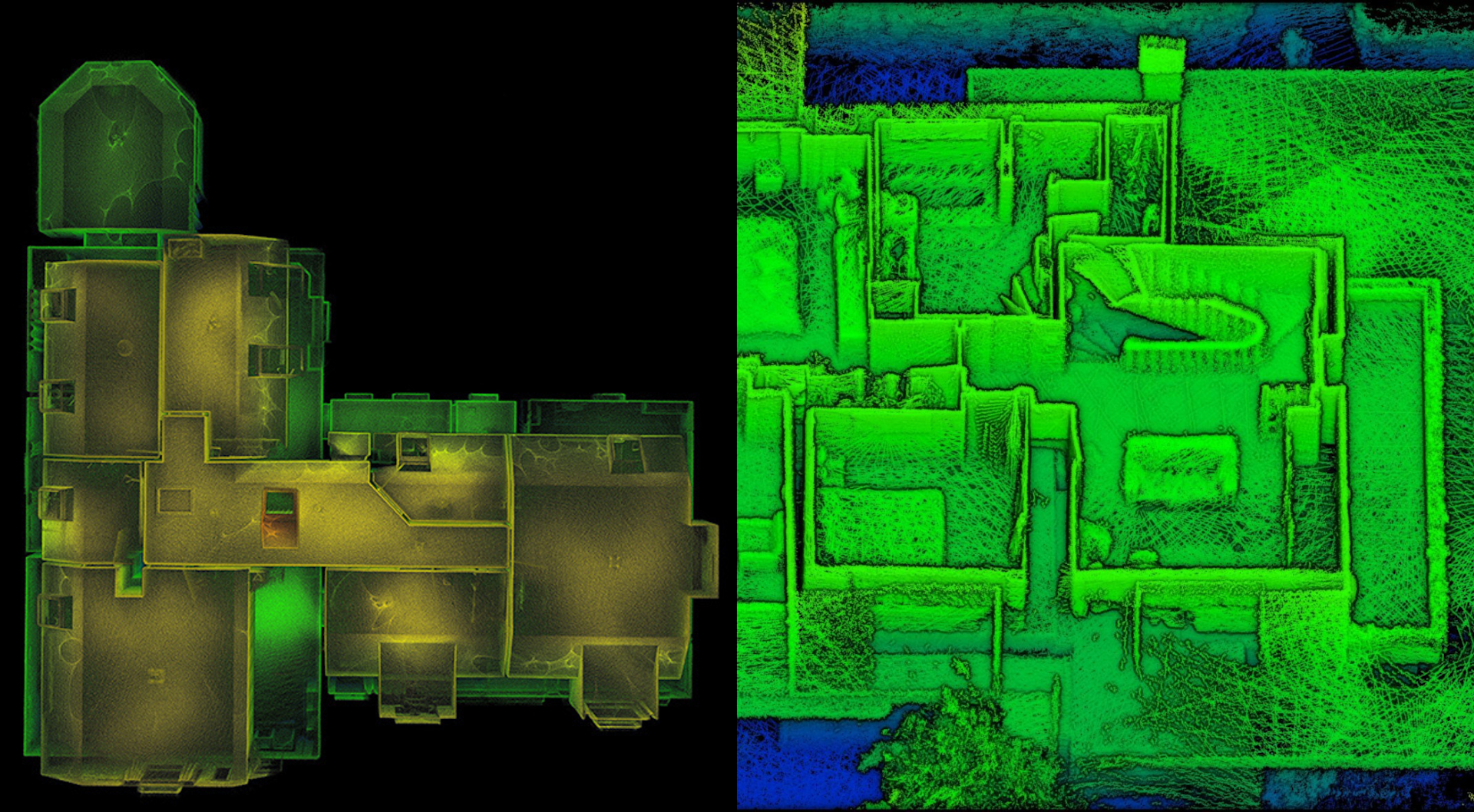
Meanwhile, SLAM devices can be useful for mapping the inside of a property, making it a beneficial solution for real estate. The example, pictured below, was captured using the handheld GeoSLAM ZEB Go sensor.
3: Mobility
SLAM systems are highly mobile and facilitate on-the-go mapping, capturing huge swathes of data on the move.
Simply walk - or fly - through an environment to build a map: No longer do you need to worry about time-consuming set up, being confined to a dedicated position or needing to constantly reposition hardware like total stations or other traditional equipment.
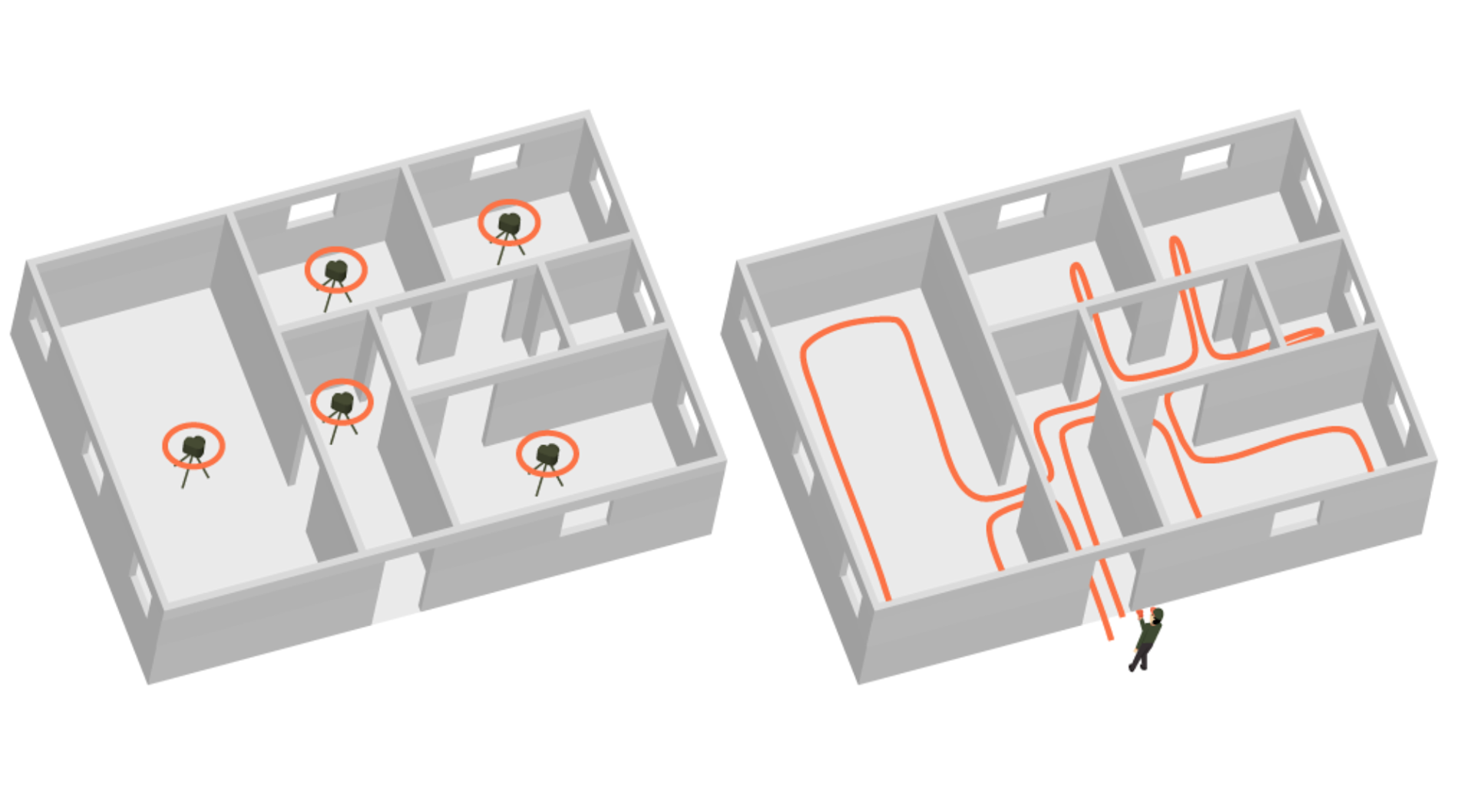
SLAM systems, like the GeoSLAM ZEB Horizon, can be integrated into vehicles or mobile platforms - like drones - for efficient mapping of roads, infrastructure, and urban areas.
This also makes SLAM sensors ideal for rapid scanning. For instance, GeoSLAM solutions can be used to create or update a BIM model up to 10 times faster than traditional scanners, making it an ideal technique for monitoring construction processes.
GNSS-LiDAR Surveying Benefits And Applications
1: Accurate Absolute Positioning
GNSS-based LiDAR systems have global coordinate systems natively embedded, which results in achieving direct absolute positioning to acquire the precise geographic coordinates of each LiDAR point.
That's not to say that this cannot be achieved with SLAM LiDAR, but extra steps are generally needed with this type of surveying.
This can include:
Setting up reflective ground control targets, which can be time-consuming and difficult to do in areas with poor accessibility;
Adding additional hardware, such as integrating the ZEB Locate (pictured below) - which produces a georeferenced point cloud when the data is post-processed - to the ZEB Horizon. But this requires additional outlay on purchasing the accessory and it stops the ZEB Horizon from being drone-mounted.
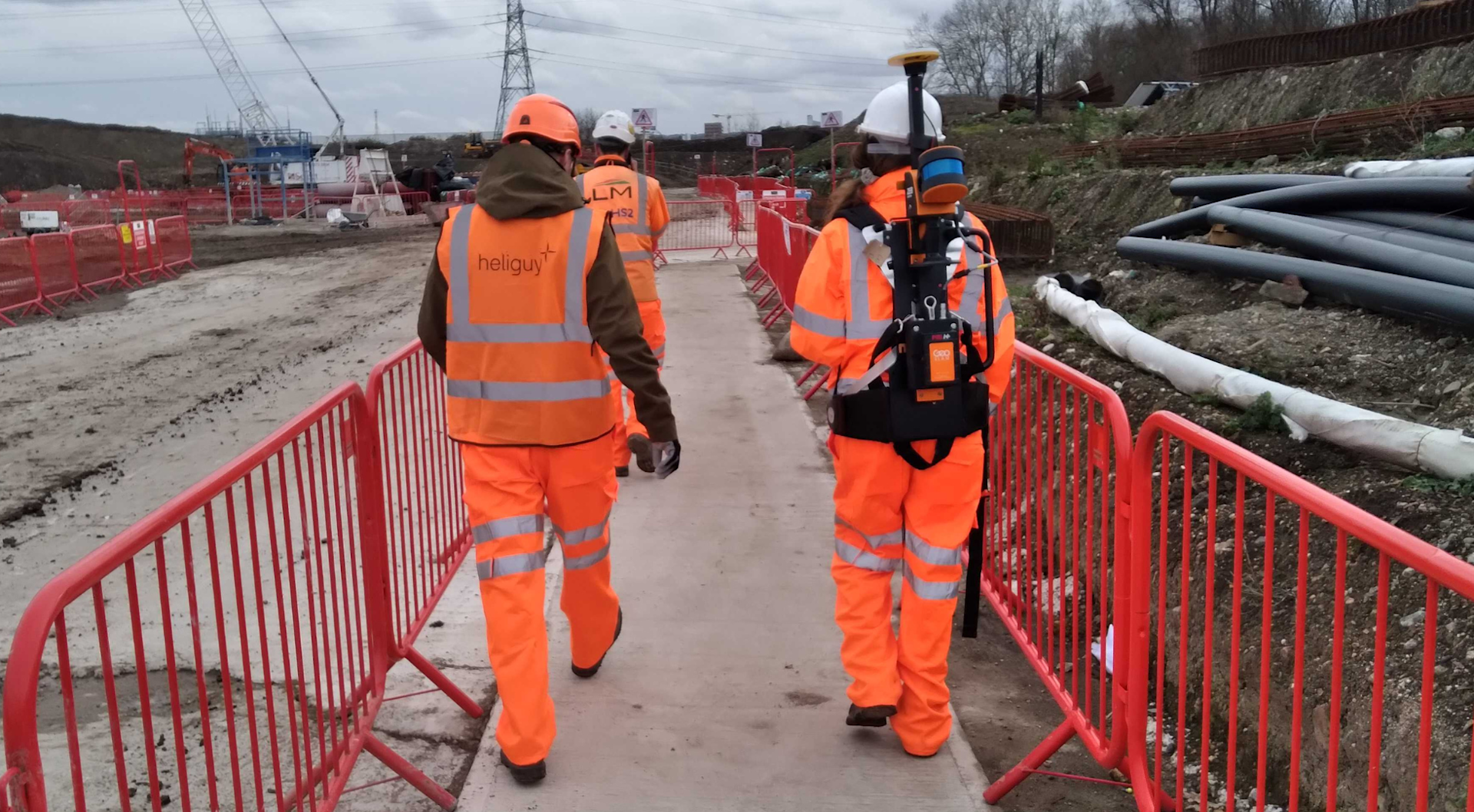

2: Data Repeatability
Data which contains GNSS absolute positioning is beneficial as it enables surveyors to go back to the same site, capture additional data from the same site and assess change easily. This includes overlaying datasets for periodical surveys.
And in the case of a large-scale infrastructure project, the project would tend to be set on a coordinate reference system, so having a directly georeferenced LiDAR point cloud provides enhanced reliability and workflow efficiency.
As mentioned before, this is still possible with SLAM-based LiDAR, but the process is not as streamlined and requires more manual input.
3: Elevation Mapping, Terrain Modelling And Object Detection
GNSS LiDAR sensors usually have the ability to support multiple returns, compared to SLAM payloads, which typically don't have this capability.
It means that GNSS sensors are generally able to collect more comprehensive and detailed DTMs and penetrate vegetation canopies more effectively, along with improved object detection.
With this in mind, GNSS-based LiDAR can be useful for environmental studies, such as forest inventory, coastline mapping, and monitoring land-use changes.
For instance, this Digital Elevation Model at Pagham Harbour shows a large shingle spit which was a significant factor in a retreating coastline in the area. This data - captured using the DJI Zenmuse L1 - was used as part of efforts to help monitor and mitigate coastal erosion. Read the full case study here.
SLAM Vs GNSS For LiDAR: Best Solutions
We've already touched on some of the best SLAM and GNSS solutions for LiDAR mapping, but in this section, we'll explore these in more detail.
Best SLAM Solutions
When it comes to SLAM surveying, heliguy™ has partnered with GeoSLAM to offer its ecosystem of mapping hardware and software.
The GeoSLAM LiDAR scanning solutions are the ZEB Go, ZEB Revo RT, and ZEB Horizon. They can be used for handheld, go any-where mapping, and are compatible with a range of accessories to enhance data collection, such as adding 360° panoramic photos to scans and colour to point clouds. They are also all IP-rated to operate in adverse weather conditions.
For added versatility, the ZEB Horizon - which is the most powerful GeoSLAM sensor with an enhanced range, more sensors, and ability to scan more points per second, can be integrated with a drone or a vehicle. The image below shows the ZEB Horizon attached to a DJI M300 RTK.
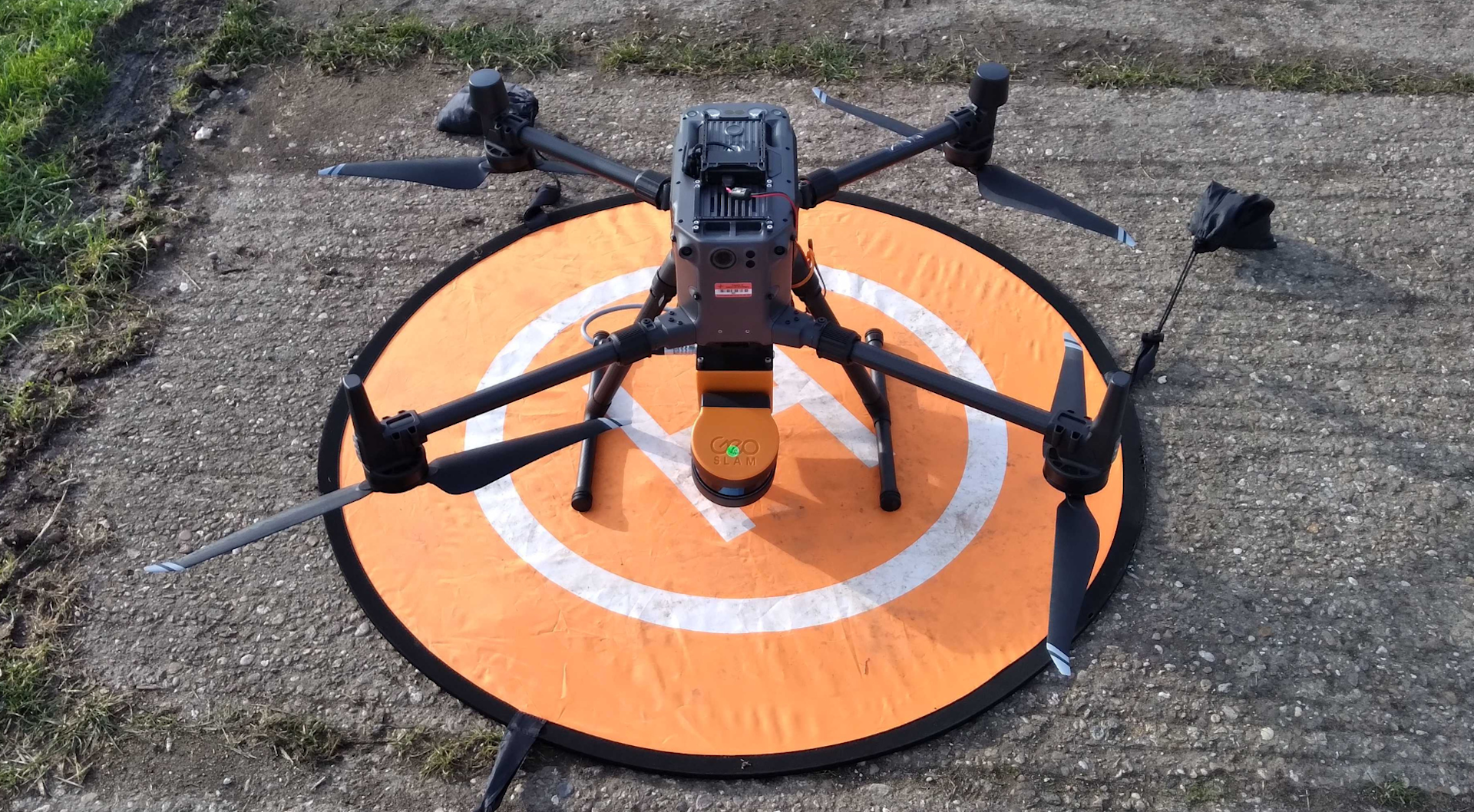

The ZEB Horizon can also be upgraded to the ZEB Horizon RT (essentially a phone mount), which enables real-time data capture previews.
For a full comparison between the GeoSLAM sensors, click here.
Best GNSS-LiDAR Solution
The DJI Zenmuse L1 is a cost-effective, plug-and-play drone LiDAR solution, compatible with the DJI M300 Series.

Its key features include:
Integrates a LiDAR module, RGB camera (for colourised point clouds and photogrammetry missions), and high-accuracy IMU;
Generate true-colour point cloud models in real-time;
Acquire 2 kilometre-squared of point cloud data in a single flight;
Render centimetre-accurate reconstructions thanks to the high-accuracy IMU, a vision sensor for positioning accuracy, and the incorporation of GNSS data;
Point rate of 240,000 pts/s, 3 returns support, and non-repetitive and repetitive scanning pattern helps build a dense digital terrain model in densely vegetated areas;
The IP54 rating allows the L1 to be operated in rainy or foggy environments. The LiDAR module’s active scanning method enables you to fly at night.
Summary
Selecting between SLAM and GNSS solutions for LiDAR mapping depends on the specific requirements of the surveying project. For indoor surveys, GNSS-denied areas, or for rapid, on-the-go mapping, SLAM technology provides an advantage.
On the other hand, GNSS-based LiDAR offers native accurate absolute positioning and can benefit surveyors with multi-return capabilities.
In certain scenarios, a hybrid approach that combines SLAM and GNSS-based LiDAR may be beneficial. This allows surveyors to leverage the real-time mapping capabilities of SLAM along with the streamlined precise positioning of GNSS-based LiDAR, providing comprehensive and accurate surveying results.
Understanding the strengths and applications of SLAM and GNSS for LiDAR surveying empowers surveying professionals to select the most appropriate technology for their specific needs.
By leveraging these advanced surveying approaches, professionals can enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and effectiveness of their surveying endeavours.
And these workflows can be bolstered by deploying industry-leading solutions from GeoSlLAM and DJI.
To discuss any of the solutions mentioned in this article, and/or to find out how the heliguy™ in-house surveying department can start/scale your surveying programme, including through dedicated survey training, contact us.

written by
James Willoughby
James joined heliguy™ in 2018 following a 13-year stint in print and online journalism, having worked on regional and weekly newspaper titles. He is responsible for spearheading heliguy™'s content strategy and social media delivery. James collaborates with DJI Enterprise's European marketing team to coordinate and produce case studies and helps organise events and webinars.